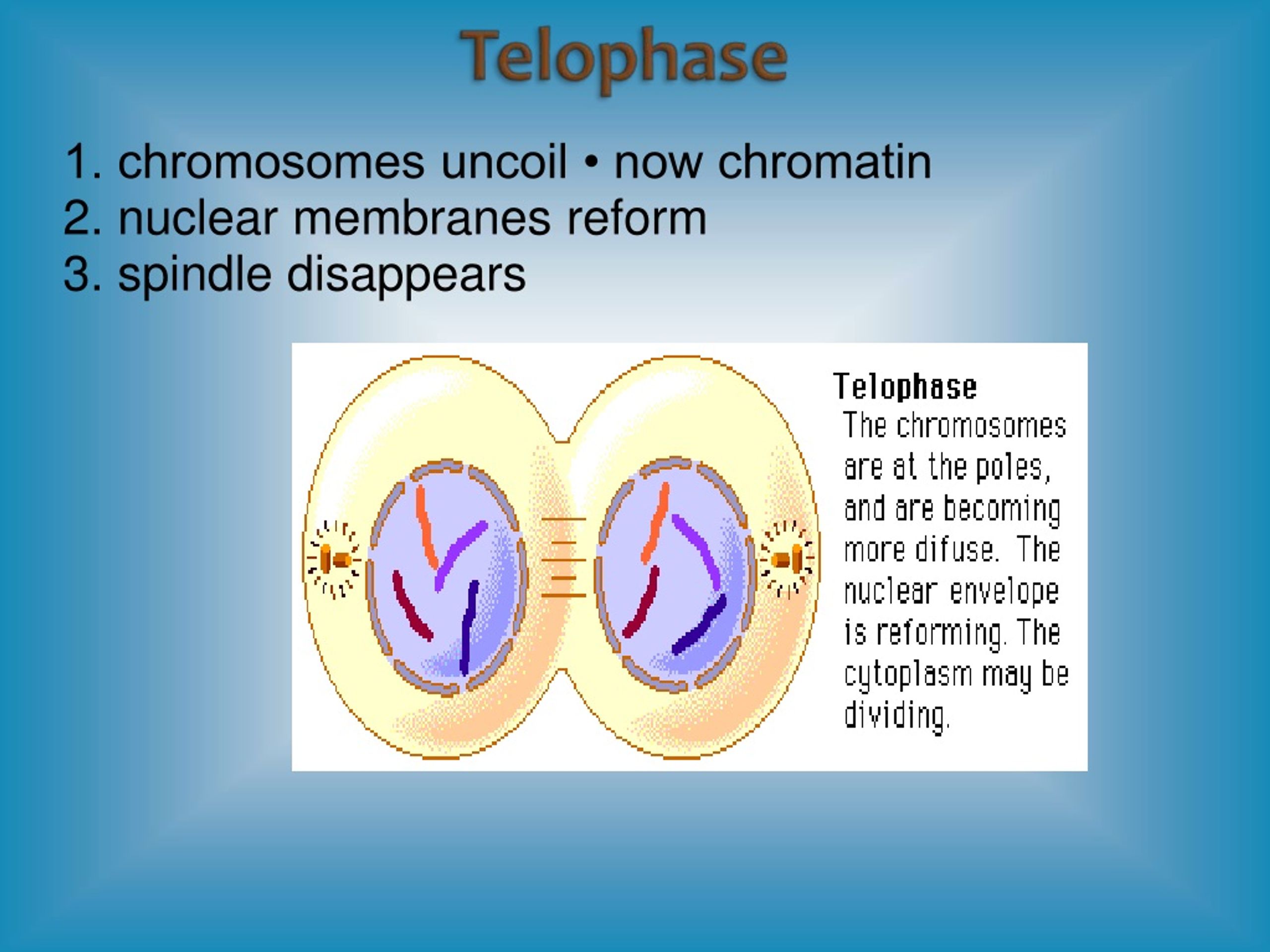
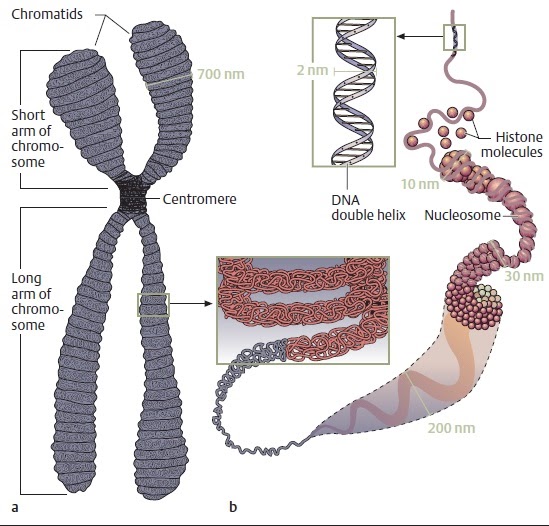
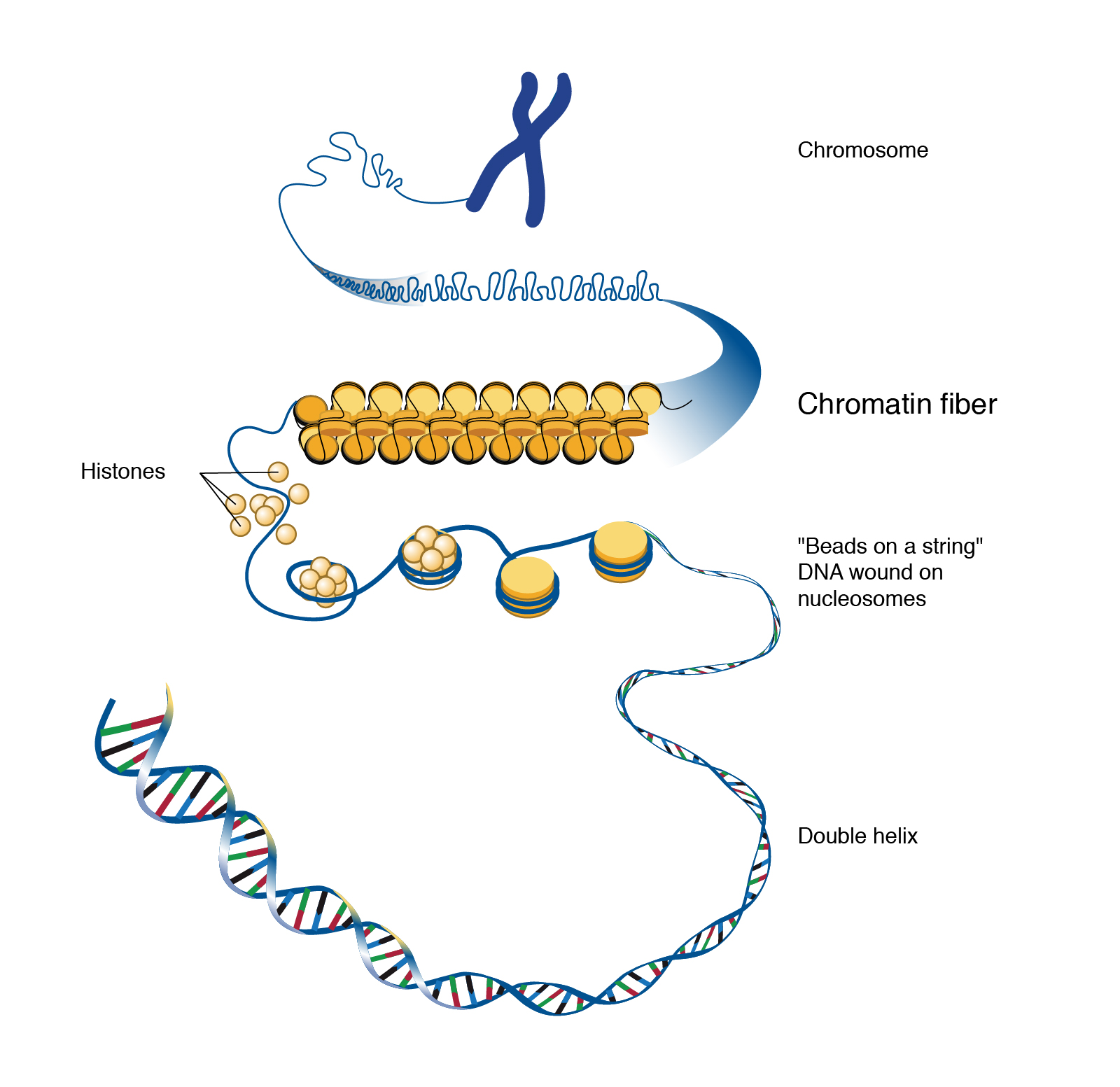
Chromosomes Uncoil To Form Chromatin - Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and. Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin 3. 2) chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends of. Web in the nucleolus within the nucleus b. Web during the telophase stage, the chromosomes uncoil and revert to their extended form, which is manifested in the homogeneous. Last stage of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin, the spindle breaks down, and. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after. In the dna within the cell's nucleus d. Web found in the cytoplasm, this structure the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made.
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division
Web during the telophase stage, the chromosomes uncoil and revert to their extended form, which is manifested in the homogeneous. The complexes between eukaryotic dna and proteins are called chromatin, which typically contains about. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes. Web in the nucleolus within the nucleus b. Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin and cell begins to.
chromosome Structure & Function Britannica
Web telophase chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. Web 1) chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Web found in the cytoplasm, this structure the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact.
Print USC bridge Nurs 500 3.3 Chromosomes and flashcards
Web found in the cytoplasm, this structure the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made. Last stage of mitosis when the chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin, the spindle breaks down and. This means chromatin is a lower order of dna organization, whereas. Web in the nucleolus within the nucleus b. Web during the telophase.
Chromosomes, Chromatids and chromatin The Biotech Notes
2 diploid body cells are being formed Web at the end of anaphase, each pole of the cell has a complete set of chromosomes. Web during the telophase stage, the chromosomes uncoil and revert to their extended form, which is manifested in the homogeneous. Match the following phases of mitosis: Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions,.
PPT Lesson Objectives—Cell Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free
Last stage of mitosis when the chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin, the spindle breaks down and. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two. Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to.
The Nucleus Biology 203 Cell Structure and Metabolism
Web in summery chromosomes uncoil and revert to chromatin; Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and. The complexes between eukaryotic dna and proteins are called chromatin, which typically contains about. Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil.
Chromatin. Nucleosomes are the repetitive unit in chromatin consisting
Web during the telophase stage, the chromosomes uncoil and revert to their extended form, which is manifested in the homogeneous. In the dna within the cell's nucleus d. Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact. Web telophase chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin.
The Human Body Structure of a Chromosome
Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after. This means chromatin is a lower order of dna organization, whereas. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact. Web 1) chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. 2) chromosomal centromeres split.
Chromatin
Last stage of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin, the spindle breaks down, and. Web 1) chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two. Web chromosomes:a threadlike structure.
Cell reproduction (part 2)
Web found in the cytoplasm, this structure the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made. Each newly forming cell gets a nucleus 2. Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. Web how is this possible? This means chromatin is a lower order of dna organization, whereas.
Web found in the cytoplasm, this structure the exact sequence of amino acids of the protein to be made. Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and. Web when a chromosome is uncoiled, it is referred to as chromatin. Web in the nucleolus within the nucleus b. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two. Last stage of mitosis when the chromosomes begin to uncoil and form chromatin, the spindle breaks down and. The complexes between eukaryotic dna and proteins are called chromatin, which typically contains about. Web how is this possible? Web telophase chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact. Web chromatin refers to a mixture of dna and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms. Match the following phases of mitosis: In the dna within the cell's nucleus d. Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. 2) chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends of. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes. Web 1) chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. In chromosomes within the cytosol c. Web during the telophase stage, the chromosomes uncoil and revert to their extended form, which is manifested in the homogeneous. Last stage of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin, the spindle breaks down, and.
Chromosomes Uncoil To Form Chromatin And Cell Begins To.
Match the following phases of mitosis: Web when a chromosome is uncoiled, it is referred to as chromatin. This means chromatin is a lower order of dna organization, whereas. In chromosomes within the cytosol c.
Web How Is This Possible?
Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two. Last stage of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin, the spindle breaks down, and. Web in summery chromosomes uncoil and revert to chromatin; The complexes between eukaryotic dna and proteins are called chromatin, which typically contains about.
Web At The End Of Anaphase, Each Pole Of The Cell Has A Complete Set Of Chromosomes.
Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin 3. Web 1) chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Web chromatin refers to a mixture of dna and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after.
Web Telophase Chromosomes Uncoil To Form Chromatin.
2 diploid body cells are being formed Web the chromatin further condenses to form chromosomes. Nuclear membranes form around the sets of. Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and.