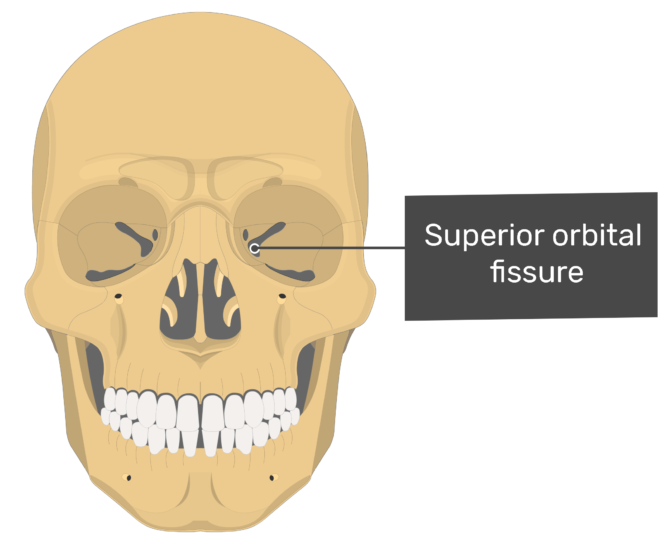
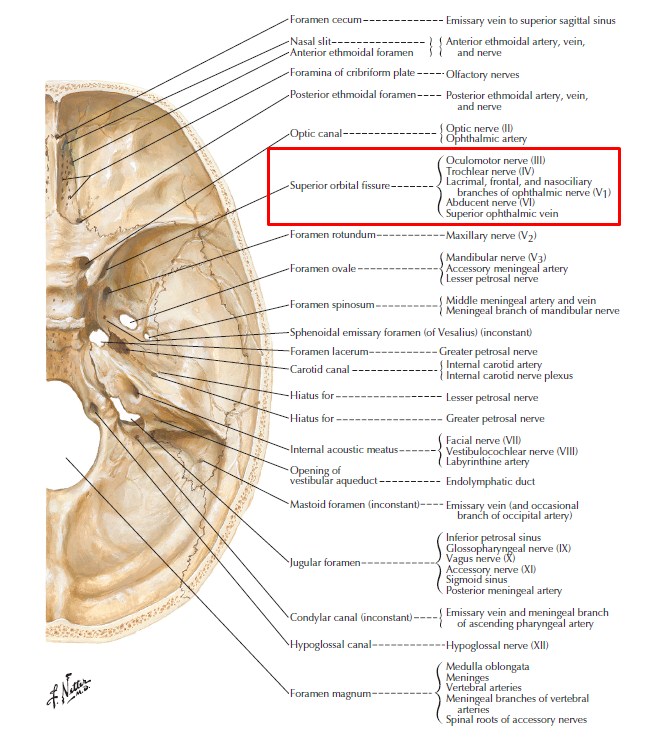
The Superior Orbital Fissure Is Formed In The Sphenoid Bone - The lateral wall comprises the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and. Orbital part of the frontal bone, lesser wing of the sphenoid bone orbital plate of the ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, frontal. It transmits the oculomotor nerve (cn iii), trochlear nerve (cn iv), ophthalmic. Web several nerves travel through the sphenoid bone’s foramina, fissures, and canal. It is formed by the zygoma. Web in this study, the microsurgical anatomy and morphometry of the superior orbital fissure and its related structures were examined. Web the superior orbital fissure opens anteriorly into the orbit. Web the bony orbit is formed by several bones of the skull, including the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone,. Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. Web the inferior orbital fissure is the inferolateral continuation of superior orbital fissure.
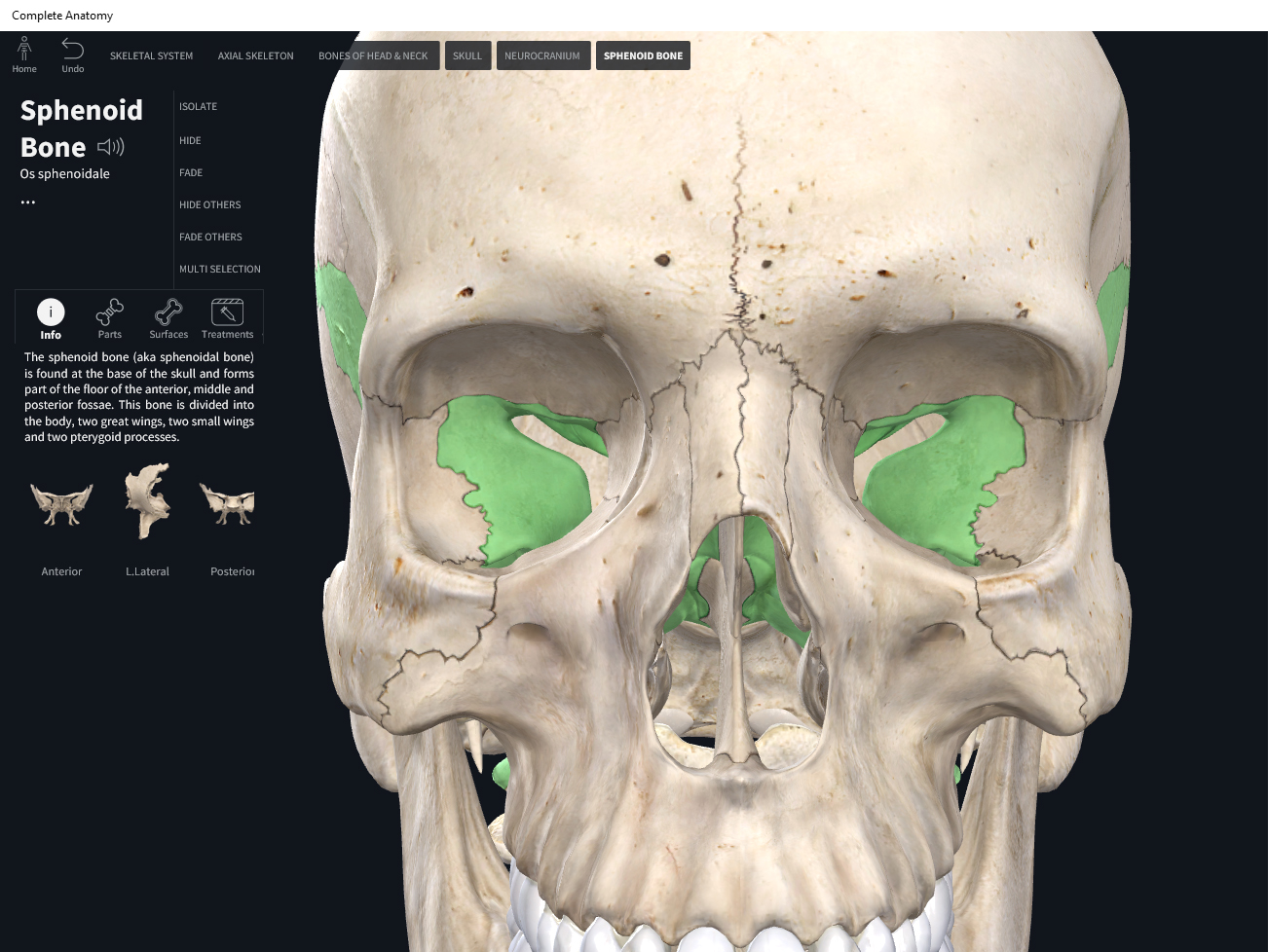
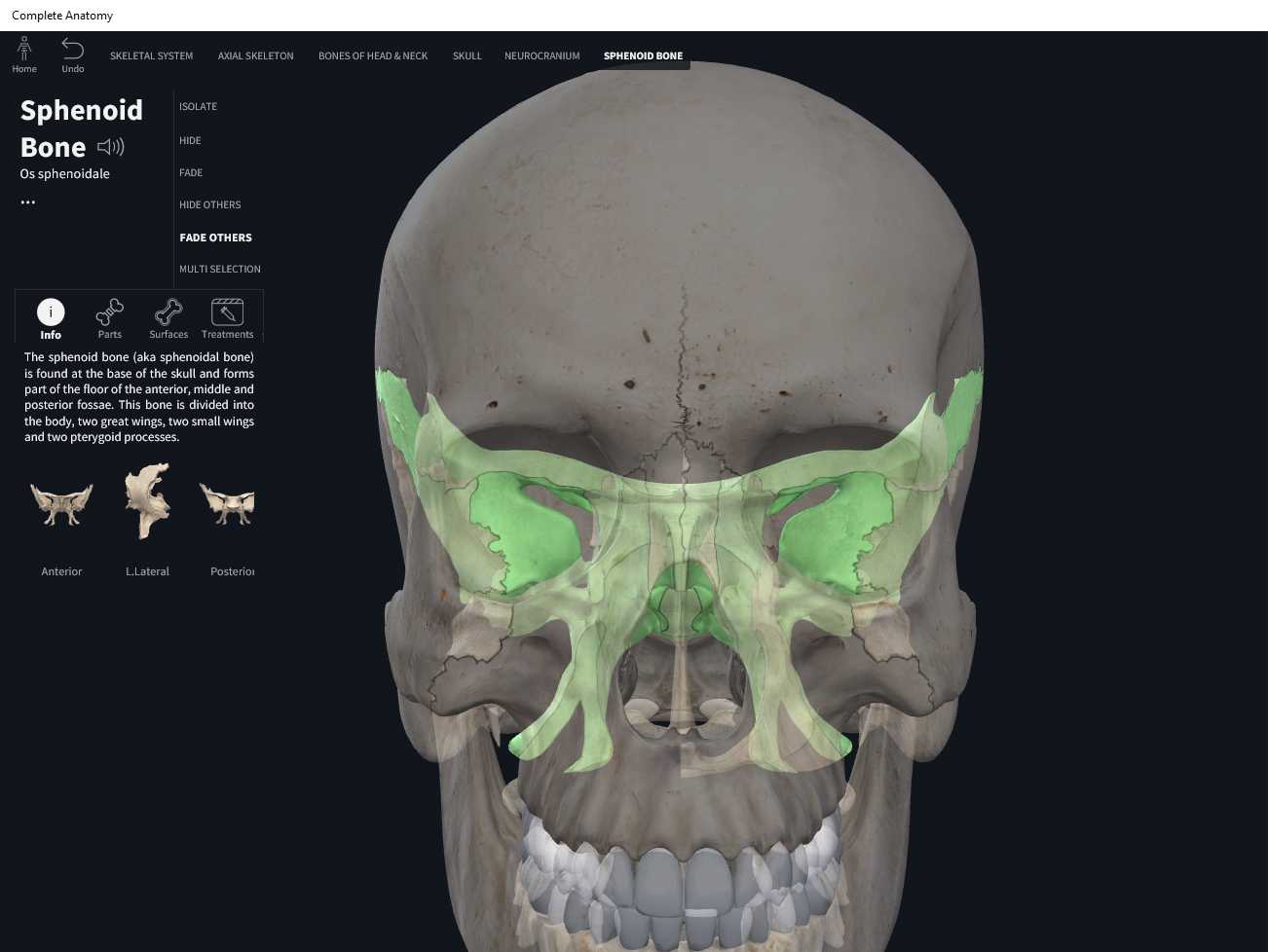
Sphenoid Bone
It is formed by the zygoma. Web the inferior orbital fissure (iof) lies in the floor of the orbit inferior to the superior orbital fissure and it is. Web the foramen rotundum (plural: Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. Web foramen rotundum foramen ovale superior.
right orbit bones Human anatomy and physiology, Anatomy, Rectus muscle
Web in this study, the microsurgical anatomy and morphometry of the superior orbital fissure and its related structures were examined. Web the bony orbit is formed by several bones of the skull, including the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone,. Web for example, the superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. Foramina rotunda).
Bones Skull, sphenoid. Anatomy & Physiology
Web the superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. Web the superior orbital fissure is the communication between the cavernous sinus and the apex of the orbit. Web in this study, the microsurgical anatomy and morphometry of the superior orbital fissure and its related structures were.
What is superior orbital fissure syndrome?
Web for example, the superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. The optic canal enables the optic. Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. It is formed by the zygoma. Web the superior surface of the sphenoid body contains.
Facial Fracture Management Handbook Applied Anatomy Iowa Head and
Web foramen rotundum foramen ovale superior oblique muscle internal auditory meatus external acoustic meatus most popular. The optic canal enables the optic. Web the bony orbit is formed by several bones of the skull, including the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone,. Web the inferior orbital fissure is the inferolateral continuation of superior orbital fissure. Web the superior surface of.
Image result for anterior parietal bone presentation Facial nerve
Web the superior orbital fissure is the communication between the cavernous sinus and the apex of the orbit. Web the superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. Web the bony orbit is formed by several bones of the skull, including the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid.
Bones Skull, sphenoid. Anatomy & Physiology
Web the foramen rotundum (plural: Web several nerves travel through the sphenoid bone’s foramina, fissures, and canal. Web the superior orbital fissure opens anteriorly into the orbit. Web in this study, the microsurgical anatomy and morphometry of the superior orbital fissure and its related structures were examined. Web the superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull.
Orbital Roof — Ophthalmology Review
The inferior surface of small wings of sphenoid forms the back part of the roof of the orbit, and the upper boundary of. The zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid. Web the lateral orbital wall is formed by two bones: Web the inferior orbital fissure (iof) lies in the floor of the orbit inferior to the superior.
Foramen spinosum is an anatomical structure foramen in sphenoid bone
The inferior surface of small wings of sphenoid forms the back part of the roof of the orbit, and the upper boundary of. Web the inferior orbital fissure is the inferolateral continuation of superior orbital fissure. Web several nerves travel through the sphenoid bone’s foramina, fissures, and canal. Web the optic strut represents a bony formation that connects the body.
Sphenoid Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. Web several nerves travel through the sphenoid bone’s foramina, fissures, and canal. Web in this study, the microsurgical anatomy and morphometry of the superior orbital fissure and its related structures were examined. The optic canal enables the optic. Web.
Web sella turcica articulations the sphenoid articulates with the frontal, parietal, ethmoid, temporal, zygomatic, palatine, vomer, and. Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. Web several nerves travel through the sphenoid bone’s foramina, fissures, and canal. Web the lateral orbital wall is formed by two bones: The lateral wall comprises the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and. It is formed by the zygoma. Web the inferior orbital fissure is the inferolateral continuation of superior orbital fissure. Web the superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. Web in this study, the microsurgical anatomy and morphometry of the superior orbital fissure and its related structures were examined. Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. Web the superior orbital fissure opens anteriorly into the orbit. An unpaired bone located in the cranium (or skull), the sphenoid bone, also known as the “wasp. Web the superior surface of the sphenoid body contains some important bony landmarks: Web for example, the superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. Web the orbital roof is formed by the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. Web the foramen rotundum (plural: Foramina rotunda) is located in the middle cranial fossa, inferomedial to the superior. Web the optic strut represents a bony formation that connects the body of sphenoid bone and its lesser wing and separates optic canal. Web the superior orbital fissure is the communication between the cavernous sinus and the apex of the orbit. Web the bony orbit is formed by several bones of the skull, including the frontal bone, sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone,.
Web The Superior Orbital Fissure Is Formed In The Sphenoid Bone, Whereas The Inferior Orbital Fissure Is Formed Between The Sphenoid.
Web for example, the superior orbital fissure lies between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. Web the superior orbital fissure is the communication between the cavernous sinus and the apex of the orbit. It is formed by the zygoma. It transmits the oculomotor nerve (cn iii), trochlear nerve (cn iv), ophthalmic.
Web The Bony Orbit Is Formed By Several Bones Of The Skull, Including The Frontal Bone, Sphenoid Bone, Ethmoid Bone,.
The optic canal enables the optic. Orbital part of the frontal bone, lesser wing of the sphenoid bone orbital plate of the ethmoid bone, lacrimal bone, frontal. Web the superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. The inferior surface of small wings of sphenoid forms the back part of the roof of the orbit, and the upper boundary of.
Web In This Study, The Microsurgical Anatomy And Morphometry Of The Superior Orbital Fissure And Its Related Structures Were Examined.
Foramina rotunda) is located in the middle cranial fossa, inferomedial to the superior. An unpaired bone located in the cranium (or skull), the sphenoid bone, also known as the “wasp. Web sella turcica articulations the sphenoid articulates with the frontal, parietal, ethmoid, temporal, zygomatic, palatine, vomer, and. Web the inferior orbital fissure (iof) lies in the floor of the orbit inferior to the superior orbital fissure and it is.
Web The Orbital Roof Is Formed By The Lesser Wing Of The Sphenoid Bone And The Frontal Bone.
Web the superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid. Web the superior orbital fissure opens anteriorly into the orbit. Web the optic strut represents a bony formation that connects the body of sphenoid bone and its lesser wing and separates optic canal. Web the inferior orbital fissure is the inferolateral continuation of superior orbital fissure.