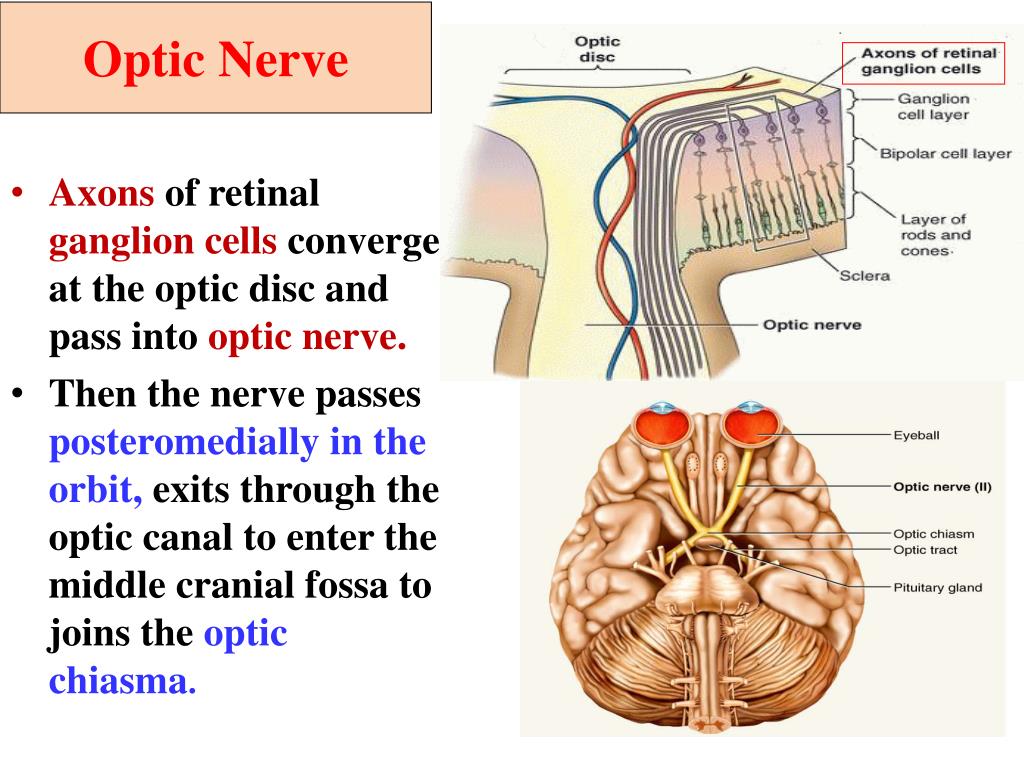
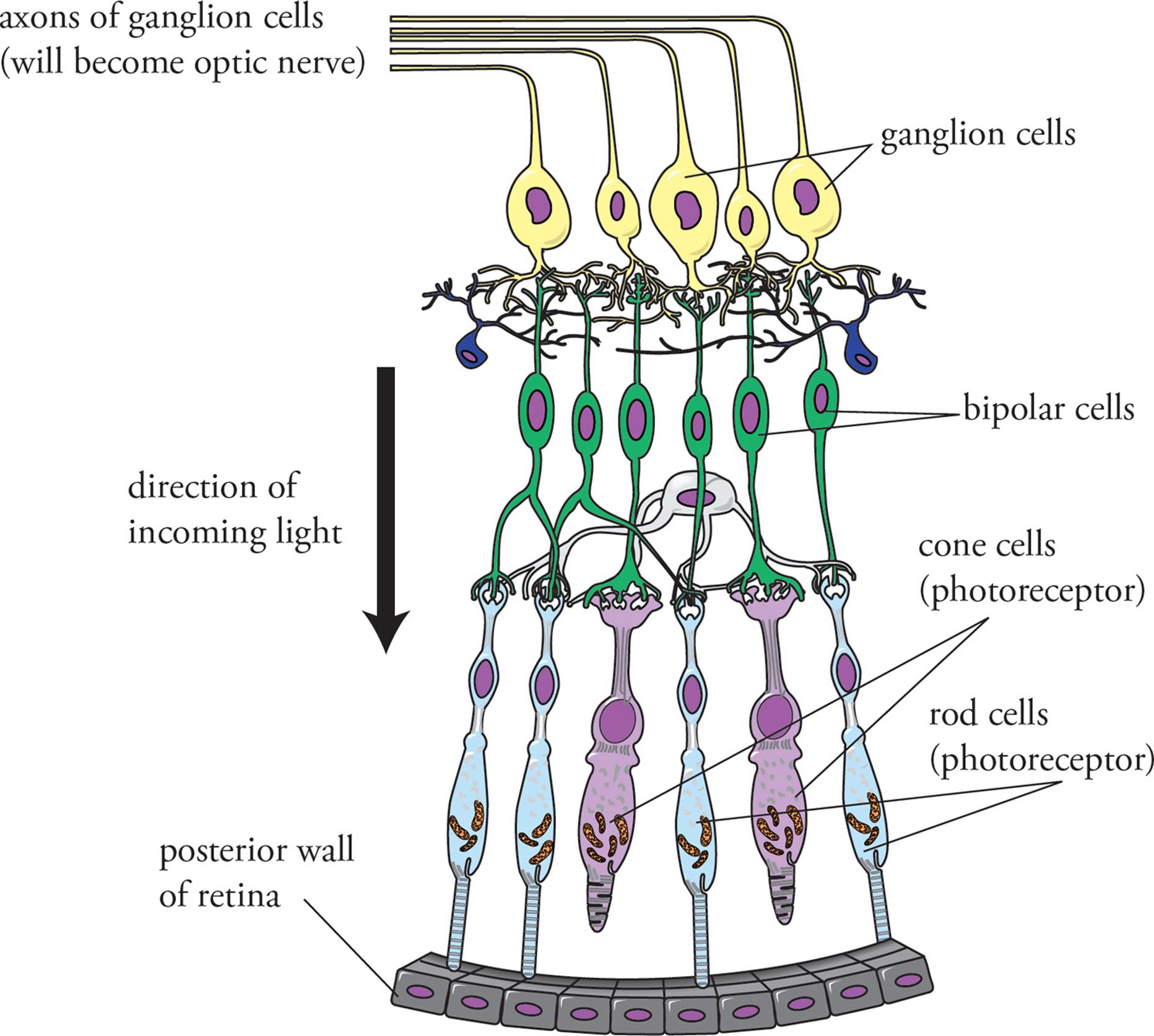
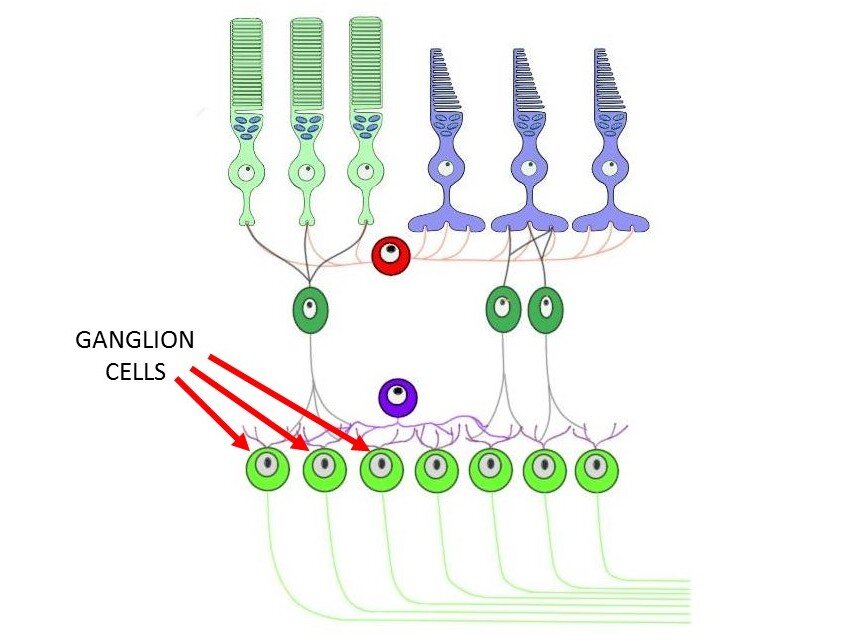
The Axons Of Ganglion Cells Converge To Form - Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the., which carries the visual information to the. Web ganglion cells are larger on average than most preceding retinal inter neurons and have large diameter axons capable of passing the electrical. Web the pathway is composed of the axons of a single neuronal cell type, the retinal ganglion cell (rgc), that navigate. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and. Web each pathway is formed by the axons of a separate type of retinal output neuron (retinal ganglion cell). The only body involved in processing visual information is the visual cortex. A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of. Web ganglion cell axons exit the retina through a circular region in its nasal part called the optic disk (or optic papilla), where they. Web retinal cells found in the inner synaptic layer that make synaptic contacts with bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and one another.
Anatomy and Physiology The Peripheral Nervous System
Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells (rgcs), astrocytes, and blood vessels are the principal constituents of the rnfl (fig. A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies. Web the axons from these ganglion cells segregate in the optic nerve and the.
PPT Cranial nerves II,III, IV,VI and Visual Pathway PowerPoint
Web f ganglion cells (291) t/f: [noun] a small cystic tumor connected either with a joint membrane or tendon sheath. Web each pathway is formed by the axons of a separate type of retinal output neuron (retinal ganglion cell). Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Web ganglion cell axons exit the retina.
Schematic illustration of retinal cell layers. RPE cells (brown
Web the pathway is composed of the axons of a single neuronal cell type, the retinal ganglion cell (rgc), that navigate. Web retinal cells found in the inner synaptic layer that make synaptic contacts with bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and one another. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of. Web here we report that ganglion cell.
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems MCAT Biology and Biochemistry
Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells (rgcs), astrocytes, and blood vessels are the principal constituents of the rnfl (fig. Web here we report that ganglion cell axons exposed to tetrodotoxin (ttx) to block neuronal activity during fetal life fail. Blind spot where this nerve leaves. Web f ganglion cells (291) t/f: Web ganglion cell axons exit the retina through.
hillis2e_ch34
Web test your knowledge of the axons of ganglion cells converging to form the optic nerve, the auditory nerve, or the olfactory epithelium. Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Web retinal cells found in the inner synaptic layer that make synaptic contacts with bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and one another. Web the.
Ganglion cell definition — Neuroscientifically Challenged
Web retinal cells found in the inner synaptic layer that make synaptic contacts with bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and one another. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of. Web here we report that ganglion cell axons exposed to tetrodotoxin (ttx) to block neuronal activity during fetal life fail. The only body involved in processing visual information.
Unmyelinated axons and retinal glia A. Ganglion cell axons within the
Web the pathway is composed of the axons of a single neuronal cell type, the retinal ganglion cell (rgc), that navigate. Web each pathway is formed by the axons of a separate type of retinal output neuron (retinal ganglion cell). Web ganglion cell axons exit the retina through a circular region in its nasal part called the optic disk (or.
Why Retinal Ganglion Cells Are Important in Vision Magazine
Axons converge to form optic nerve. Web the axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve. Web ganglion cells are larger on average than most preceding retinal inter neurons and have large diameter axons capable of passing the electrical. Web the initial step of retinal ganglion cell (rgc) axon pathfinding involves directed growth of rgc axons toward the..
What are Ganglion Cells? (with pictures)
Web here we report that ganglion cell axons exposed to tetrodotoxin (ttx) to block neuronal activity during fetal life fail. Web a set of flashcards for learning about the anatomy and physiology of vision, including the axons of ganglion cells and their. Web the axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve. Web f ganglion cells (291) t/f:.
Visual pathway. Retinal ganglion cell axons leave each eye via the
Web ganglion cell axons exit the retina through a circular region in its nasal part called the optic disk (or optic papilla), where they. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells (rgcs) form topographic connections in the optic tectum, recreating a two. The only body involved in processing visual information is the visual cortex. The two optic nerves meet at.
Web f ganglion cells (291) t/f: The two optic nerves meet at the optic chiasm, where the nerve fibers. Any neuron whose cell body is located within a ganglion. Axons converge to form optic nerve. Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Web each pathway is formed by the axons of a separate type of retinal output neuron (retinal ganglion cell). Web the axons from these ganglion cells segregate in the optic nerve and the segregation remains intact all the way up. Web the initial step of retinal ganglion cell (rgc) axon pathfinding involves directed growth of rgc axons toward the. Web ganglion cells are larger on average than most preceding retinal inter neurons and have large diameter axons capable of passing the electrical. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells (rgcs), astrocytes, and blood vessels are the principal constituents of the rnfl (fig. Web a set of flashcards for learning about the anatomy and physiology of vision, including the axons of ganglion cells and their. Web retinal cells found in the inner synaptic layer that make synaptic contacts with bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and one another. A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and. The only body involved in processing visual information is the visual cortex. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of. Blind spot where this nerve leaves. [noun] a small cystic tumor connected either with a joint membrane or tendon sheath. Web crystallin optical coherence tomography inner plexiform layer retinal pigment epithelium ganglion cell layer. Web a small percentage of retinal ganglion cells contribute little or nothing to vision, but are themselves photosensitive;
Any Neuron Whose Cell Body Is Located Within A Ganglion.
Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the., which carries the visual information to the. Web here we report that ganglion cell axons exposed to tetrodotoxin (ttx) to block neuronal activity during fetal life fail. Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Web a set of flashcards for learning about the anatomy and physiology of vision, including the axons of ganglion cells and their.
Blind Spot Where This Nerve Leaves.
Web the initial step of retinal ganglion cell (rgc) axon pathfinding involves directed growth of rgc axons toward the. The only body involved in processing visual information is the visual cortex. Web the axons from these ganglion cells segregate in the optic nerve and the segregation remains intact all the way up. Web test your knowledge of the axons of ganglion cells converging to form the optic nerve, the auditory nerve, or the olfactory epithelium.
Web The Axons Of The Retinal Ganglion Cells Form The Optic Nerve.
A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of. Web ganglion cells are larger on average than most preceding retinal inter neurons and have large diameter axons capable of passing the electrical. Web retinal cells found in the inner synaptic layer that make synaptic contacts with bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and one another.
Web Ganglion Cell Axons Exit The Retina Through A Circular Region In Its Nasal Part Called The Optic Disk (Or Optic Papilla), Where They.
Web crystallin optical coherence tomography inner plexiform layer retinal pigment epithelium ganglion cell layer. Axons converge to form optic nerve. Web a small percentage of retinal ganglion cells contribute little or nothing to vision, but are themselves photosensitive; Web each pathway is formed by the axons of a separate type of retinal output neuron (retinal ganglion cell).