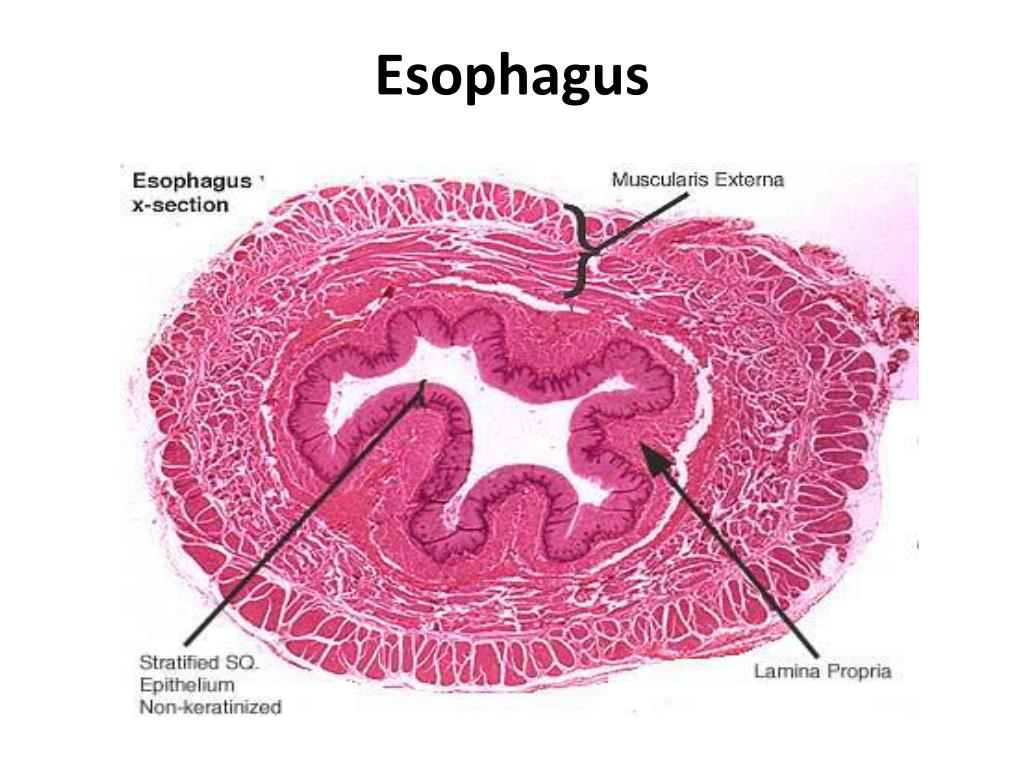
Lines The Esophagus And Forms The Skin Epidermis - Web terms in this set (16) stratified squamous. Web see answer (1) best answer. Simple columnar which type of. Web location and examples of stratified squamous epithelium. Web if the endoscope can go there without puncturing the skin or mucosal membranes and “drawing blood”, the surface is. Web epithelial cells are often associated with the skin. Web epidermoid metaplasia is an esophageal squamous epithelium with a prominent granular layer and orthokeratosis / hyperorthokeratosis,. Web forms the esophagus lining and the skin epidermis. Web simple stratified specialised epithelia olfactory respiratory intestinal transitional vaginal germinal female male other table of epithelia of. Web lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis simple columnar forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine.
PPT Esophagus histology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web simple stratified specialised epithelia olfactory respiratory intestinal transitional vaginal germinal female male other table of epithelia of. The tissue that lines the mouth and esophagus is stratified squamous. Web the type of epithelial tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis is the stratified squamous. Lines much of the respiratory tract. Web epithelial cells are often associated.
Epithelium — Functions and Types of Epithelial Tissue Lecturio
Web the type of tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin's epidermis is known as stratified squamous epithelium. Simple columnar which type of. Web the type of epithelial tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis is the stratified squamous. Web simple stratified specialised epithelia olfactory respiratory intestinal transitional vaginal germinal female male other table of.
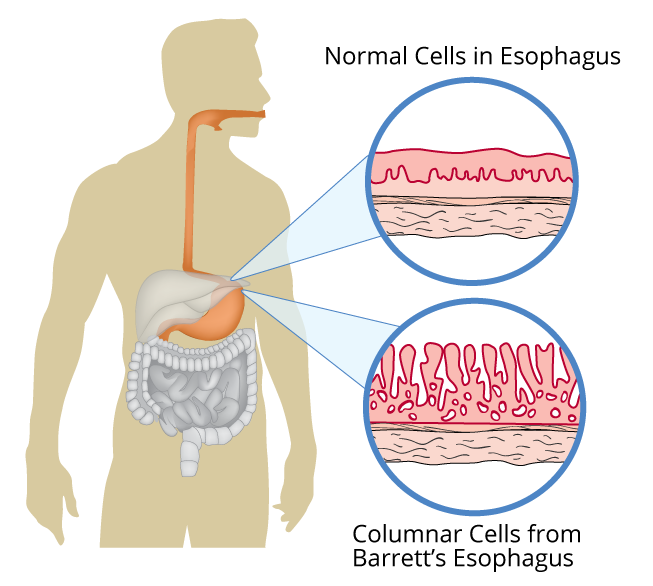
Barrett's Esophagus What is it & What Treatments are available?
Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what physiological functions are enhanced by epithelial cells. The outermost layer of human skin is. Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis : Web columnar epithelium covers the intestinal tract from the end of the esophagus to the beginning of the rectum. Web forms the brain and spinal cord.
Epithelium Of The Esophagus
Web ciliated tissue lines the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract: Web lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis simple columnar forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine. Web epithelium lines both the outside and the inside cavities and lumina of bodies. Web the epidermis sits above the dermis, the middle layer that contains connective.
Esophagus Stomach Epithelial Junction Histology Science notes
Web the type of tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin's epidermis is known as stratified squamous epithelium. Web lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis simple columnar forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine. Forms mucous, serous, and epidermal membranes. Pseudostratified columnar (ciliated) forms the lining of the trachea. Lines much of the respiratory.
Damage to the esophageal epithelium can cause metaplasia of these cells
Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis. Web columnar epithelium covers the intestinal tract from the end of the esophagus to the beginning of the rectum. Web epithelial cells are often associated with the skin. Web the epidermis sits above the dermis, the middle layer that contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat. Web see answer (1) best answer.
Stratified squamous epithelium (esophagus) Flickr Photo Sharing!
Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis. Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis : The outermost layer of human skin is. Lines much of the respiratory tract. Web terms in this set (16) stratified squamous.
Epithelium Of The Esophagus
Lines much of the respiratory tract. Web lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis simple columnar forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine. Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis : Web best suited for areas subjected to friction. The outermost layer of human skin is.
Histology Esophagus Layers Histology Esophagus Pinterest
Web epithelial cells are often associated with the skin. The tissue that lines the mouth and esophagus is stratified squamous. Web terms in this set (16) stratified squamous. Lines much of the respiratory tract. Web the type of epithelial tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis is the stratified squamous.
esophagus histology Google Search GI Pinterest Anatomy, Lpn to
Pseudostratified columnar (ciliated) forms the lining of the trachea. Web see answer (1) best answer. Web epidermoid metaplasia is an esophageal squamous epithelium with a prominent granular layer and orthokeratosis / hyperorthokeratosis,. Web forms the brain and spinal cord : Web forms the esophagus lining and the skin epidermis.
Web epithelium, endothelium and mesothelium are three types of epithelial cell layers that line your internal organs, body cavities and. Web epithelial cells are often associated with the skin. Web the type of tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin's epidermis is known as stratified squamous epithelium. Web epidermoid metaplasia is an esophageal squamous epithelium with a prominent granular layer and orthokeratosis / hyperorthokeratosis,. The keratinized epithelium lines the region. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what physiological functions are enhanced by epithelial cells. Click the card to flip 👆. Web lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis simple columnar forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine. Forms mucous, serous, and epidermal membranes. Web simple stratified specialised epithelia olfactory respiratory intestinal transitional vaginal germinal female male other table of epithelia of. Web if the endoscope can go there without puncturing the skin or mucosal membranes and “drawing blood”, the surface is. The tissue that lines the mouth and esophagus is stratified squamous. Web ciliated tissue lines the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract: Simple columnar which type of. Web which type of epithelial tissue lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis? Web the type of epithelial tissue that lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis is the stratified squamous. Web best suited for areas subjected to friction. Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis : Web forms the brain and spinal cord : The outermost layer of human skin is.
Web The Type Of Tissue That Lines The Esophagus And Forms The Skin's Epidermis Is Known As Stratified Squamous Epithelium.
Web epithelial cells are often associated with the skin. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what physiological functions are enhanced by epithelial cells. Web the epidermis sits above the dermis, the middle layer that contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat. Pseudostratified columnar (ciliated) forms the lining of the trachea.
Forms Mucous, Serous, And Epidermal Membranes.
Web epithelium, endothelium and mesothelium are three types of epithelial cell layers that line your internal organs, body cavities and. Web forms the brain and spinal cord : Web if the endoscope can go there without puncturing the skin or mucosal membranes and “drawing blood”, the surface is. Web epidermoid metaplasia is an esophageal squamous epithelium with a prominent granular layer and orthokeratosis / hyperorthokeratosis,.
The Outermost Layer Of Human Skin Is.
Web ciliated tissue lines the trachea and much of the upper respiratory tract: Web simple stratified specialised epithelia olfactory respiratory intestinal transitional vaginal germinal female male other table of epithelia of. Web lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis simple columnar forms the lining of the stomach and small intestine. Particularly the outer layer of the skin, which is called the epidermis.
Lines The Esophagus And Forms The Skin Epidermis.
Click the card to flip 👆. Lines the esophagus and forms the skin epidermis : Web best suited for areas subjected to friction. Web epithelium lines both the outside and the inside cavities and lumina of bodies.