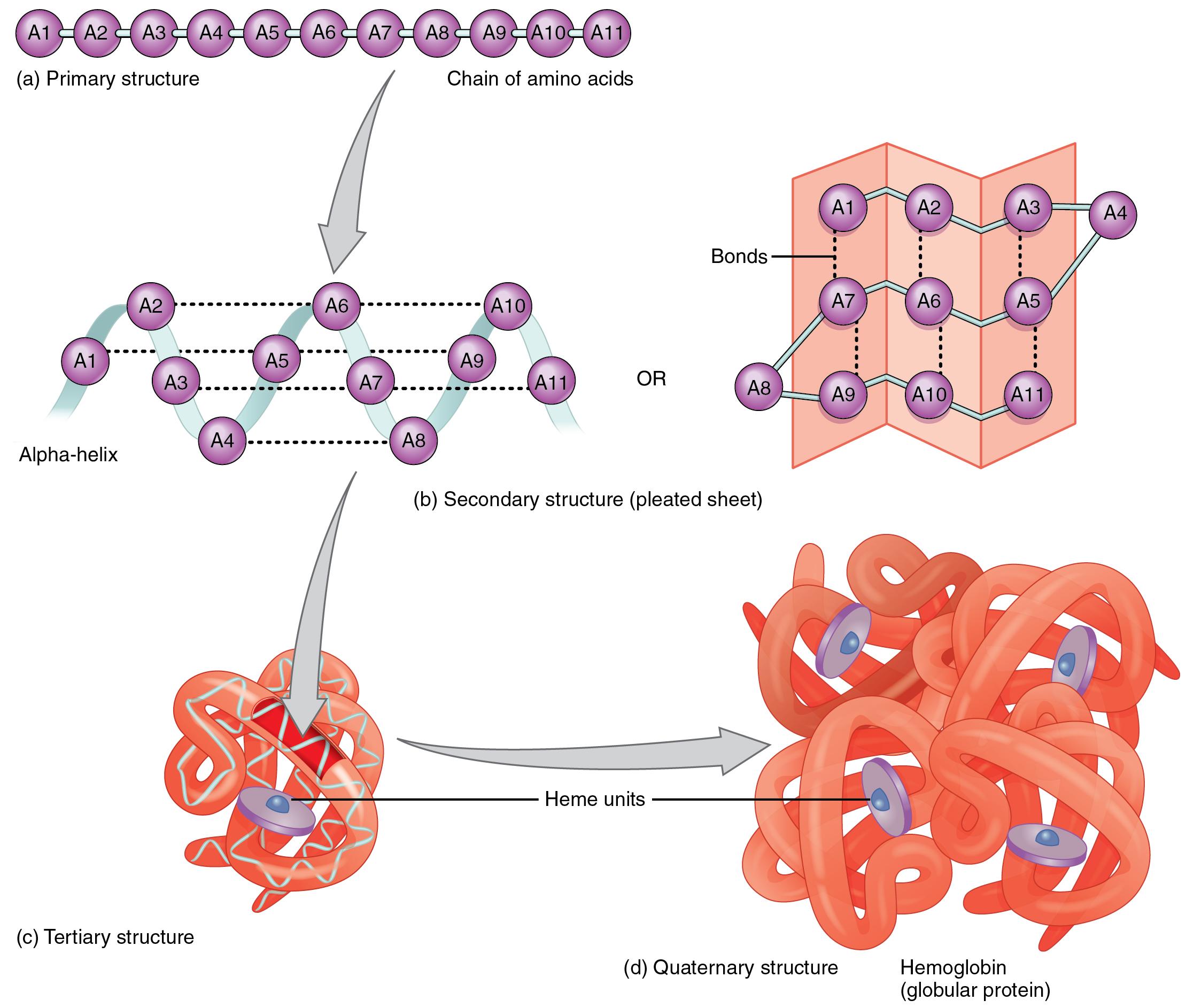
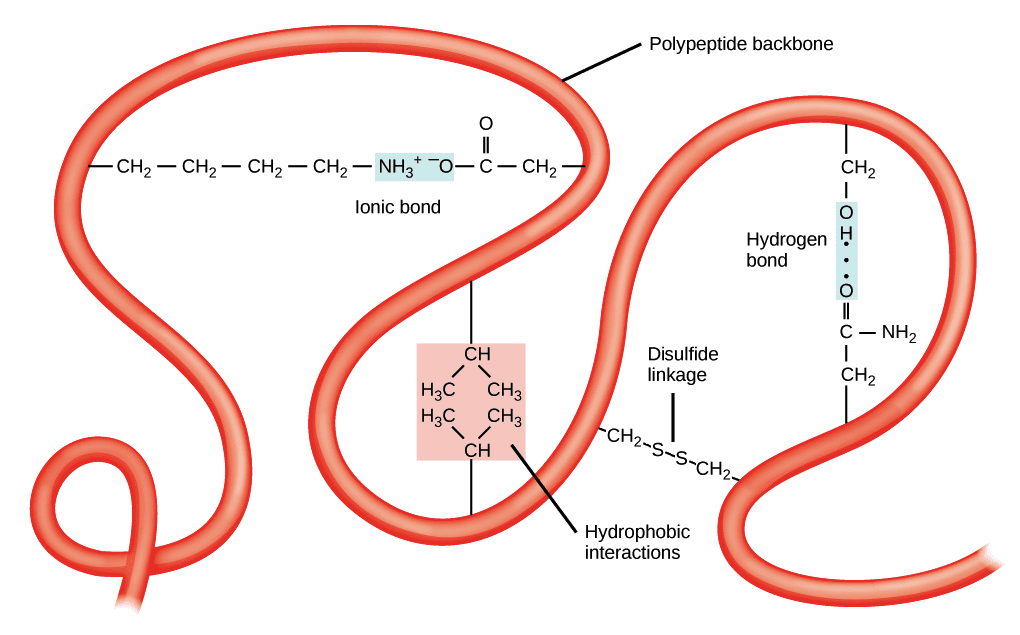
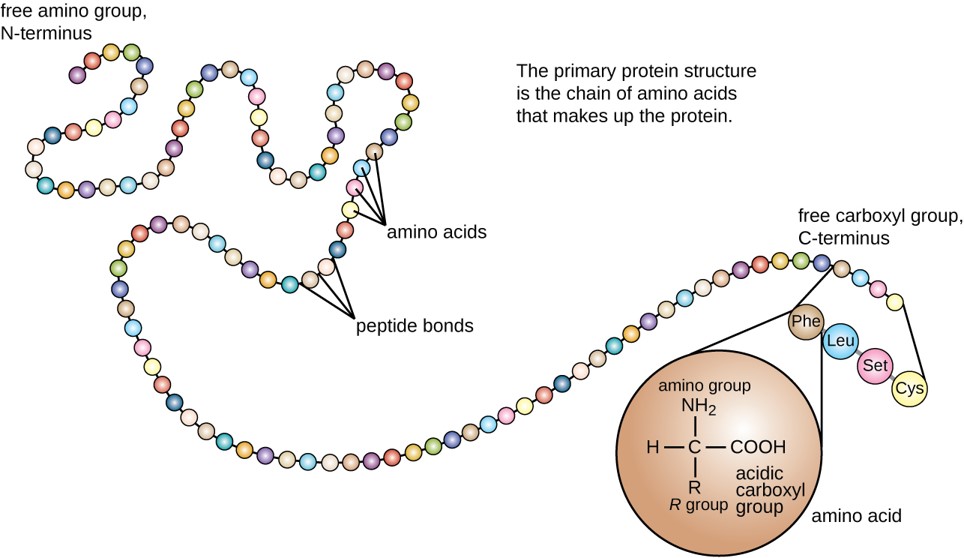
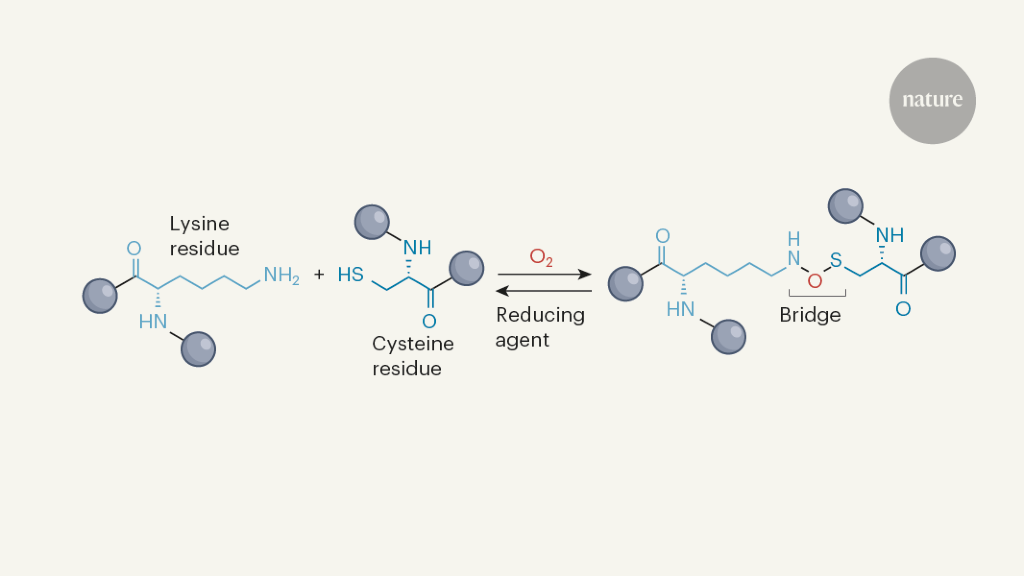
Can Form Cross Links That Stabilize Protein Structure - Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks that stabilize the protein tertiary or. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web proteins (disulfide bridges) polar, hydrophilic.
Formation of DNA−protein crosslinks conjugated to the C5 position of
Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results.
2.23 Protein Structure Nutrition Flexbook
Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web proteins (disulfide bridges) polar, hydrophilic. Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web attachment between two groups.
(PDF) Structure of the Z Ringassociated Protein, ZapD, Bound to the C
Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks.
Analysis of protein crosslinks between the identified NET proteins
Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks that stabilize the protein tertiary or. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance.
DNAProtein Crosslink Proteolysis Repair Trends in Biochemical Sciences
Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks that stabilize the protein tertiary or. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web proteins (disulfide bridges) polar, hydrophilic. Web with its well established.
What are the Stabilizing bonds Involved in Proteins
Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and.
Examples of reactive groups in DNA crosslinking to proteins
Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web proteins (disulfide bridges) polar, hydrophilic. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks that stabilize the protein tertiary or. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been.
Structure of crosslinked Grampositive bacterial peptidoglycan with
Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the.
Previously unknown type of protein crosslink discovered
Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role.
Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web molecular crosslinks known as disulfides stabilize the 3d structures of many. Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks that stabilize the protein tertiary or. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes. Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web proteins (disulfide bridges) polar, hydrophilic. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of.
Web Proteins (Disulfide Bridges) Polar, Hydrophilic.
Web with its well established compatibility with physiological systems during the last several decades, small. Web indeed, it has recently been shown that electrophilic amino acids with extended structures can selectively stabilize. Web covalent crosslinks within or between proteins play a key role in determining the structure and function of. Web the technique of chemical crosslinking has been used to enhance the stability of proteins and enzymes.
Web Molecular Crosslinks Known As Disulfides Stabilize The 3D Structures Of Many.
Web attachment between two groups on a single protein results in intramolecular crosslinks that stabilize the protein tertiary or.