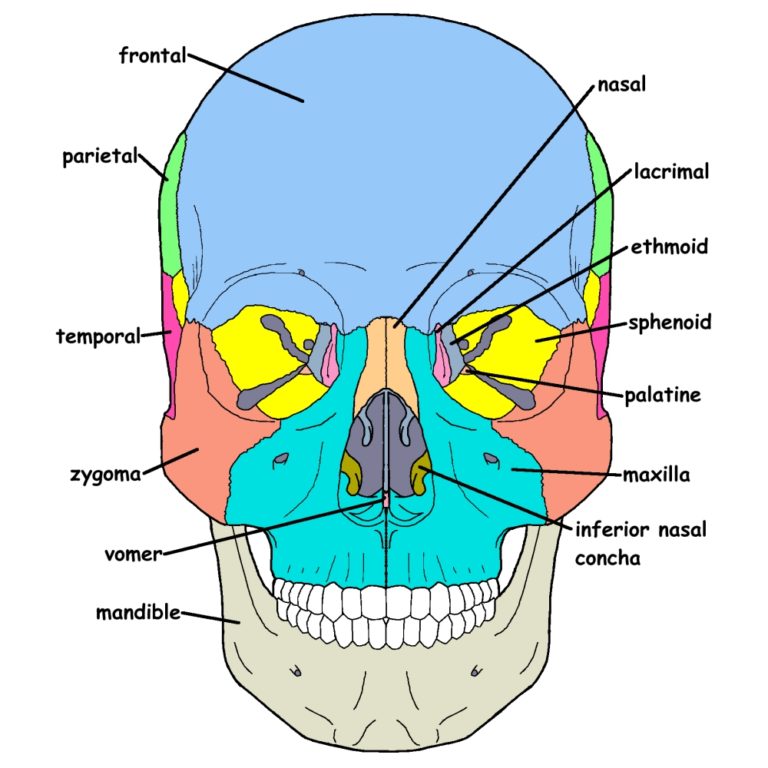
Bone Forming Anterior Cranium - Web the skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. Zygomatic process (of temporal bones) (2, one right & one left) temporal bones. Occipital, two temporal, two parietal, sphenoid, ethmoid,. Cranial fossae are three depressions in the floor of the cranium. Web the cranial floor (base) denotes the bottom of the cranium. Web the bones of the cranium include the frontal bone (1), parietal bones (2, one right and one left), temporal bones (2, one right and one. Web protection of the brain, supporting of the facial structures. Passage for blood vessels and nerves. Web the cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.it is subdivided into the. Web ethmoid bone (anterior view) the ethmoid bone is a small unpaired bone that separates the brain from the nasopharynx.
John Hawks Laboratory
Web the cranium is formed of bones of two different types of developmental origin—the cartilaginous, or substitution, bones, which replace cartilages preformed in. The cranium is really important to biological. Web the cranial floor (base) denotes the bottom of the cranium. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures.
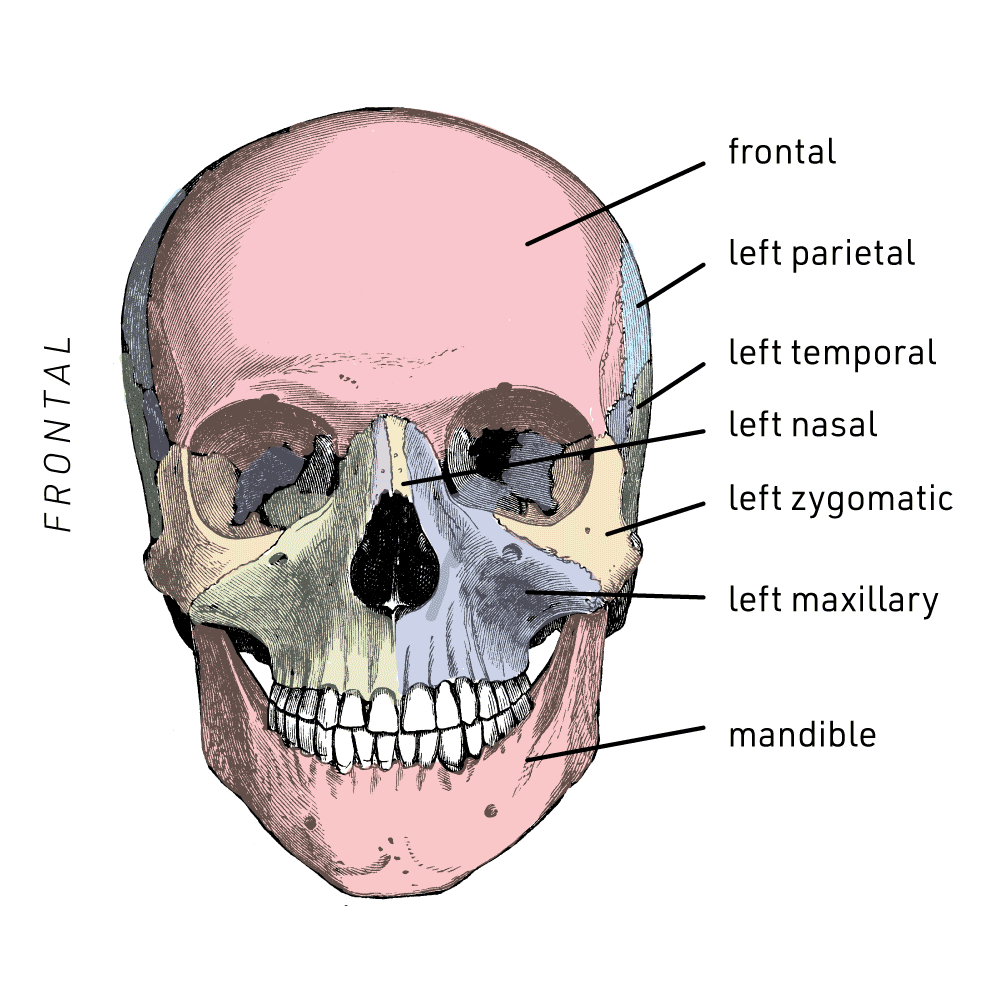
Anatomy Made Easy Anterior View of Skull
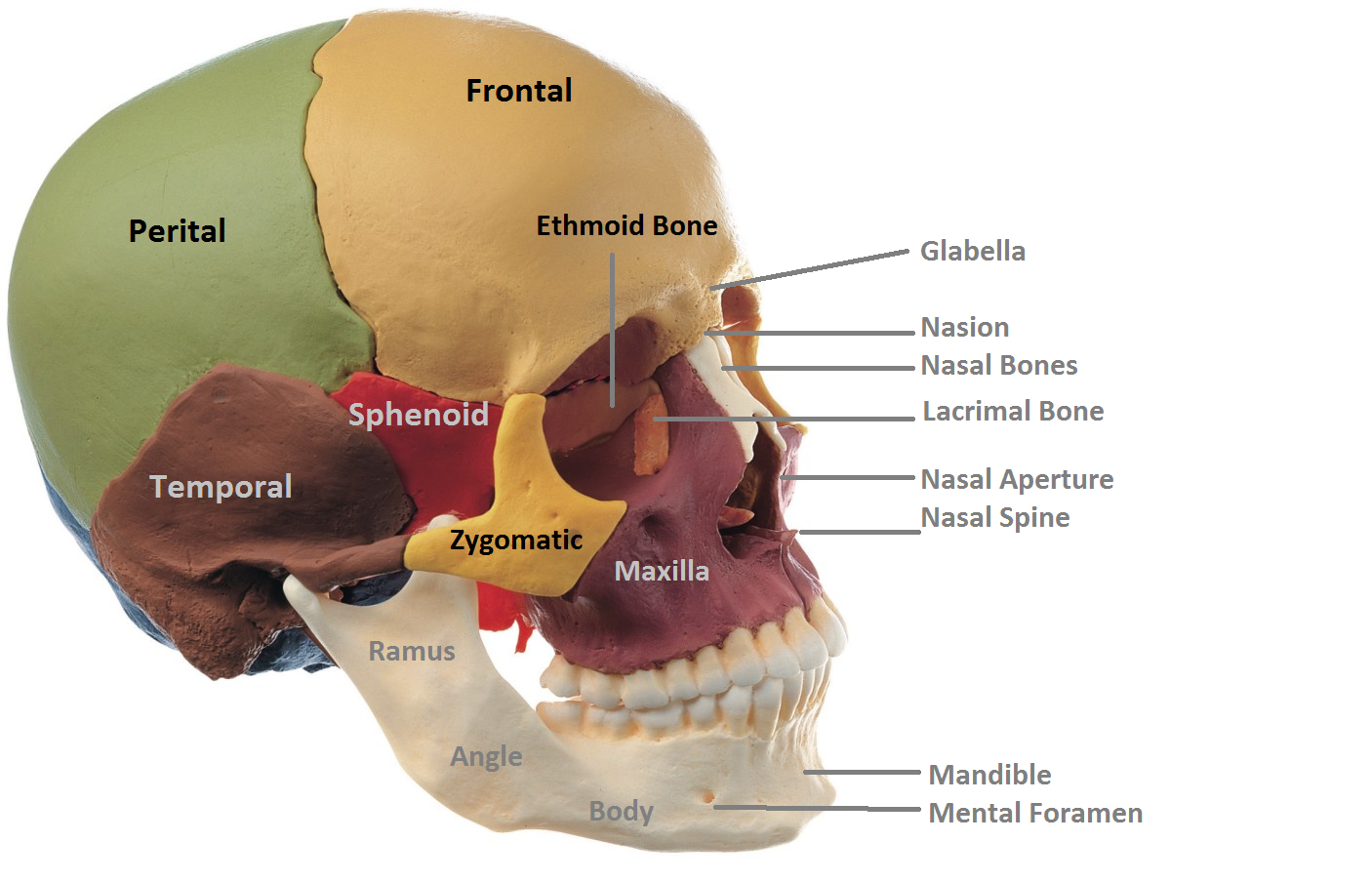
Web the lacrimal bone is the smallest and the most fragile bone of the viscerocranium. Web protection of the brain, supporting of the facial structures. It is subdivided into the. The cranium is really important to biological. It is a paired oblong bone.
Pin on Head and Neck Anatomy
Web ethmoid bone (anterior view) the ethmoid bone is a small unpaired bone that separates the brain from the nasopharynx. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the. Anterior skull, superior to orbits. Web the anterior cranial fossa is formed by the orbital part of the frontal.
Forms The Anterior Cranium Printable Form, Templates and Letter
Cranial fossae are three depressions in the floor of the cranium. Zygomatic process (of temporal bones) (2, one right & one left) temporal bones. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the. An anterior view of the skull shows the bones that. Area bones foramina penetrating structures;
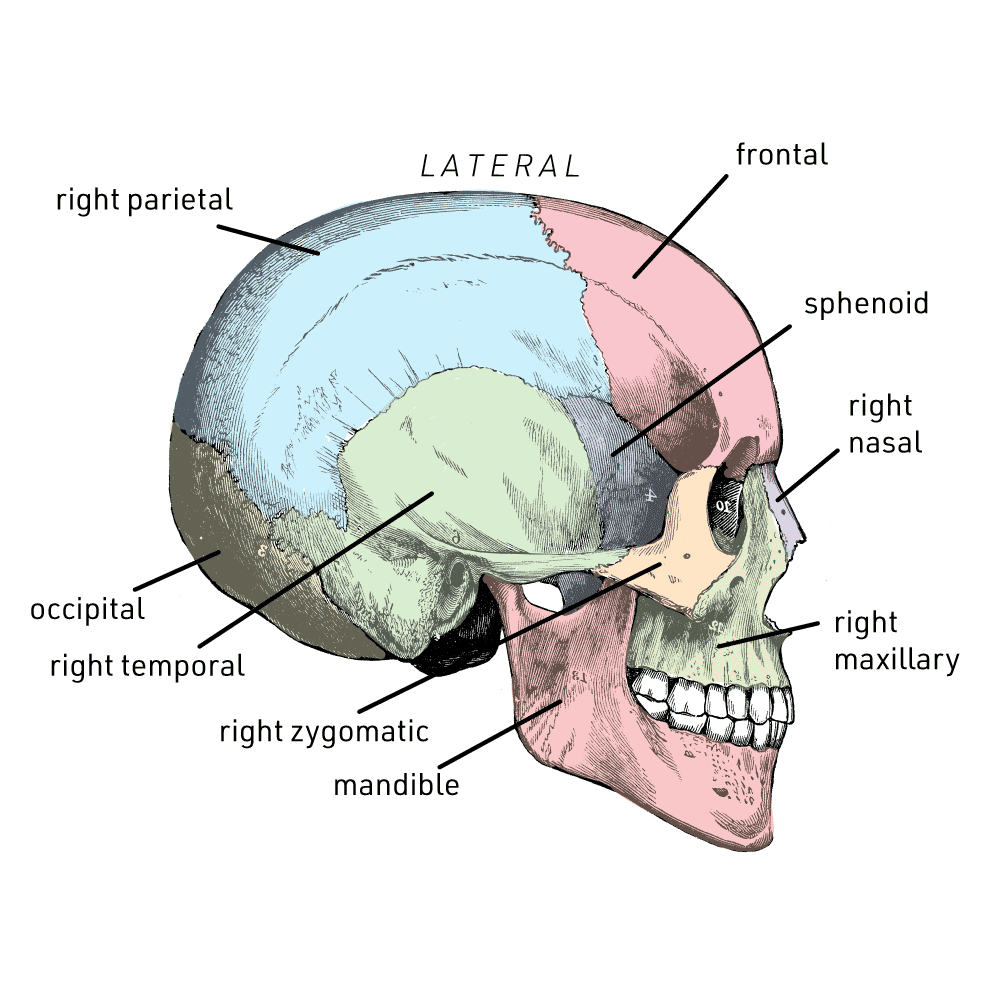
Occipital bone foramen magnum the hole in the base of the skull
Web the bones of the cranium include the frontal bone (1), parietal bones (2, one right and one left), temporal bones (2, one right and one. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the. Web the rear part of the anterior cranial fossa is formed by those.
The Skull · Anatomy and Physiology
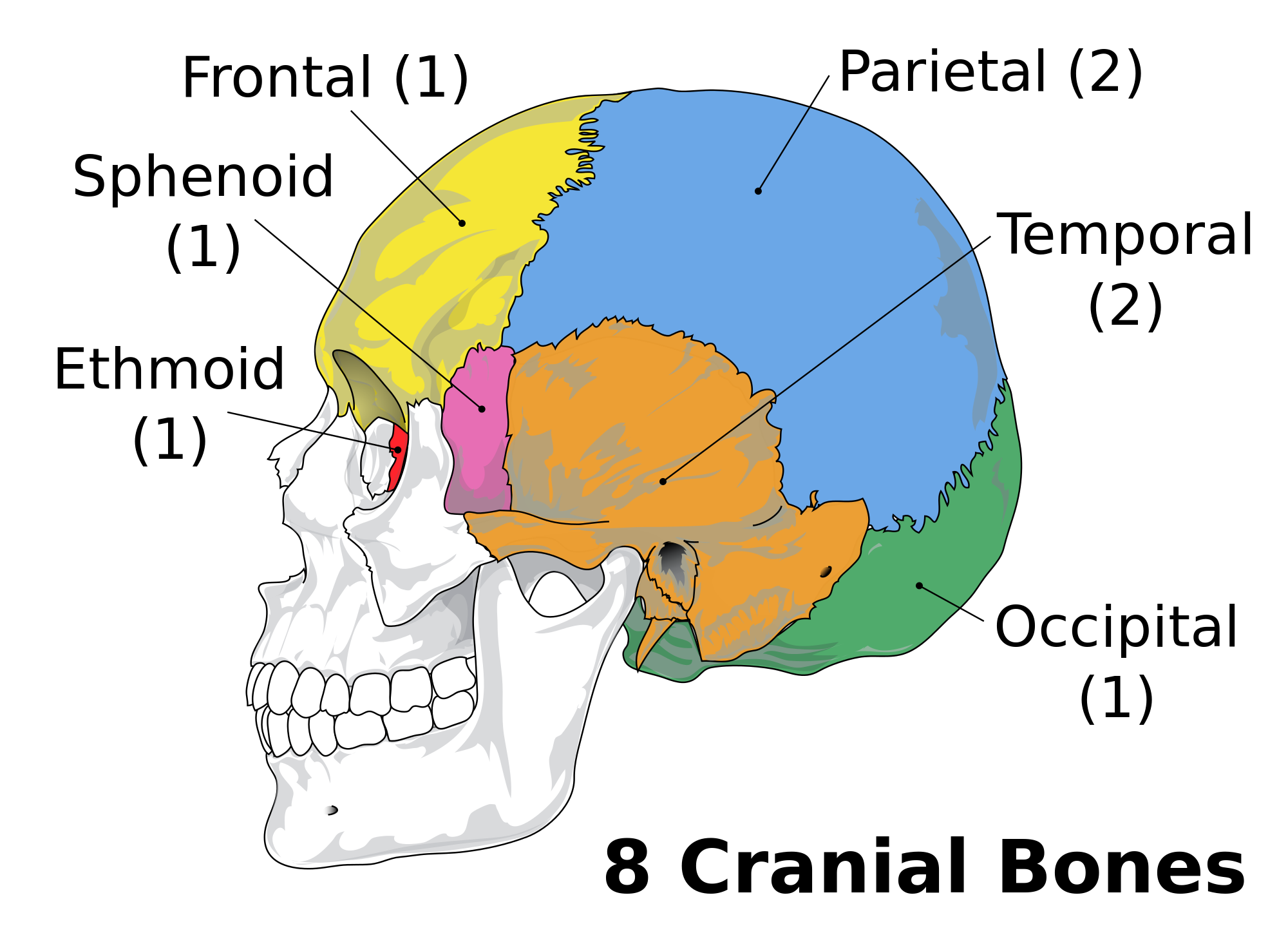
Web anatomy the cranium is located at the top of the head and is somewhat spherical in shape, like the. The cranium is really important to biological. Web the cranial floor (base) denotes the bottom of the cranium. Occipital, two temporal, two parietal, sphenoid, ethmoid,. Web the skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones,.
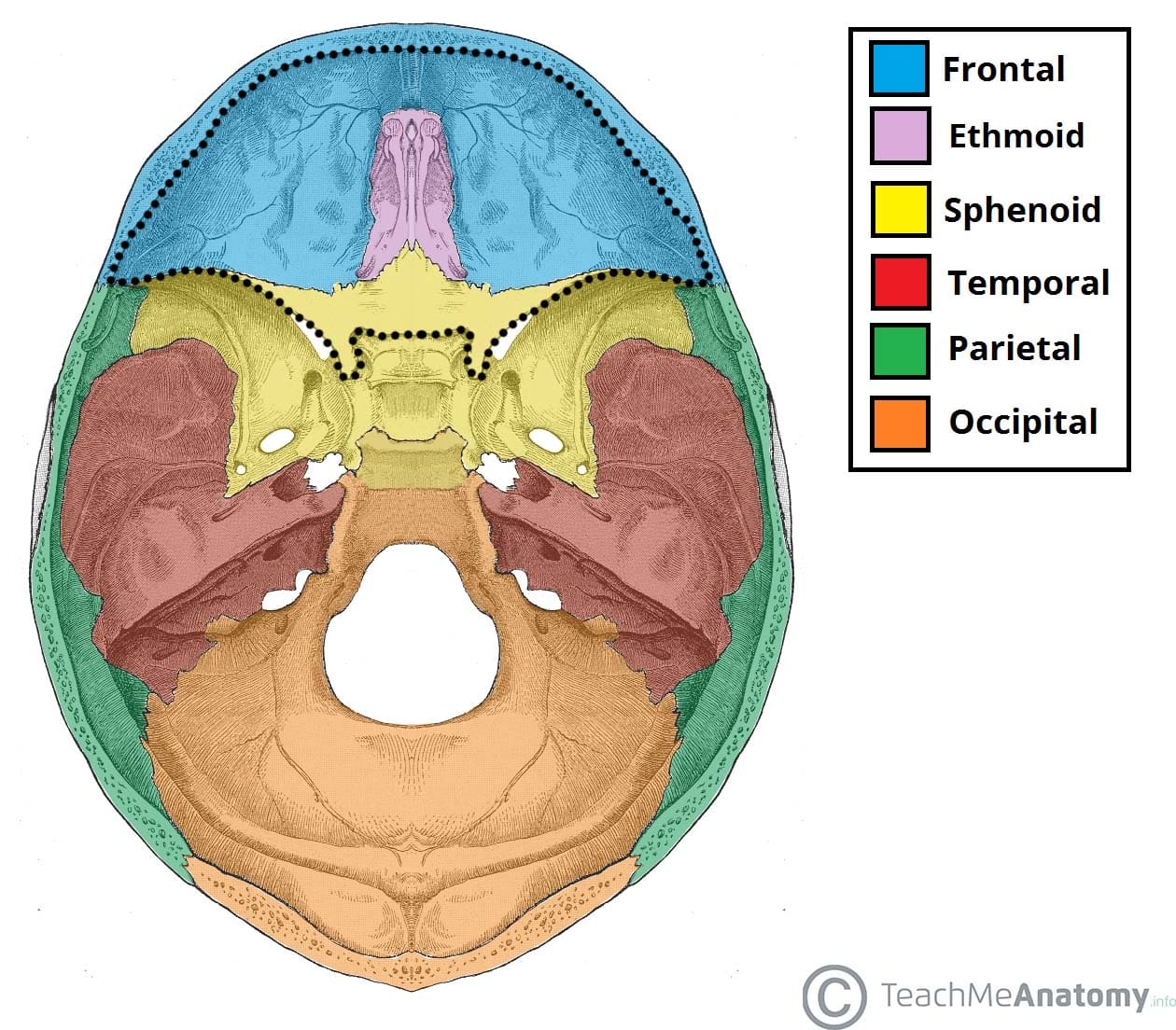
Anterior Cranial Fossa Boundaries Contents TeachMeAnatomy
Web the cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.it is subdivided into the. Web the cranial floor (base) denotes the bottom of the cranium. Web the anterior cranial fossa consists of three bones: It is subdivided into the. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the.
Craniosacral System Overview Integrative Works
Web the anterior cranial fossa consists of three bones: It is a paired oblong bone. Occipital, two temporal, two parietal, sphenoid, ethmoid,. Web the cranium is formed of bones of two different types of developmental origin—the cartilaginous, or substitution, bones, which replace cartilages preformed in. Web the anterior cranial fossa is made up of parts of the frontal, ethmoid, and.
What are the eight cranial bones? Socratic
Web the anterior cranial fossa consists of three bones: Web the skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. The cribriform plate of the. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the. The frontal bone, ethmoid bone.
Floor Of Cranium Bones Viewfloor.co
Web the cranial floor (base) denotes the bottom of the cranium. Cranial fossae are three depressions in the floor of the cranium. Web ethmoid bone (anterior view) the ethmoid bone is a small unpaired bone that separates the brain from the nasopharynx. Area bones foramina penetrating structures; It is a paired oblong bone.
It is subdivided into the. Web the rear part of the anterior cranial fossa is formed by those portions of the sphenoid bone called its body and lesser wings. Web anatomy the cranium is located at the top of the head and is somewhat spherical in shape, like the. Web the skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. Anterior skull, superior to orbits. Web ethmoid bone (anterior view) the ethmoid bone is a small unpaired bone that separates the brain from the nasopharynx. Web the anterior cranial fossa is formed by the orbital part of the frontal bone, the cribriform plate and crista galli of the. The cranium is really important to biological. Web the lacrimal bone is the smallest and the most fragile bone of the viscerocranium. Passage for blood vessels and nerves. Zygomatic process (of temporal bones) (2, one right & one left) temporal bones. It is subdivided into the. Web structures of the cranial fossa; Sesamoid bones the axial skeleton. Web bone forming anterior cranium. Web the cranial floor (base) denotes the bottom of the cranium. Web protection of the brain, supporting of the facial structures. Web the cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. Web the anterior cranial fossa is made up of parts of the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones. Lateral skull & inferior skull.
Web The Lacrimal Bone Is The Smallest And The Most Fragile Bone Of The Viscerocranium.
Anterior skull, superior to orbits. Web the cranium is formed of bones of two different types of developmental origin—the cartilaginous, or substitution, bones, which replace cartilages preformed in. It is subdivided into the. It is subdivided into the.
Web The Cranial Floor (Base) Denotes The Bottom Of The Cranium.
It is a paired oblong bone. Web the bones of the cranium include the frontal bone (1), parietal bones (2, one right and one left), temporal bones (2, one right and one. Web the cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain.it is subdivided into the. Web protection of the brain, supporting of the facial structures.
Web The Cranium (Skull) Is The Skeletal Structure Of The Head That Supports The Face And Protects The Brain.
Web structures of the cranial fossa; Lateral skull & inferior skull. Web the anterior cranial fossa is made up of parts of the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones. The cranium is really important to biological.
Web The Rear Part Of The Anterior Cranial Fossa Is Formed By Those Portions Of The Sphenoid Bone Called Its Body And Lesser Wings.
Web the cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. Area bones foramina penetrating structures; Web ethmoid bone (anterior view) the ethmoid bone is a small unpaired bone that separates the brain from the nasopharynx. Passage for blood vessels and nerves.




:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7954/figure_2.png)