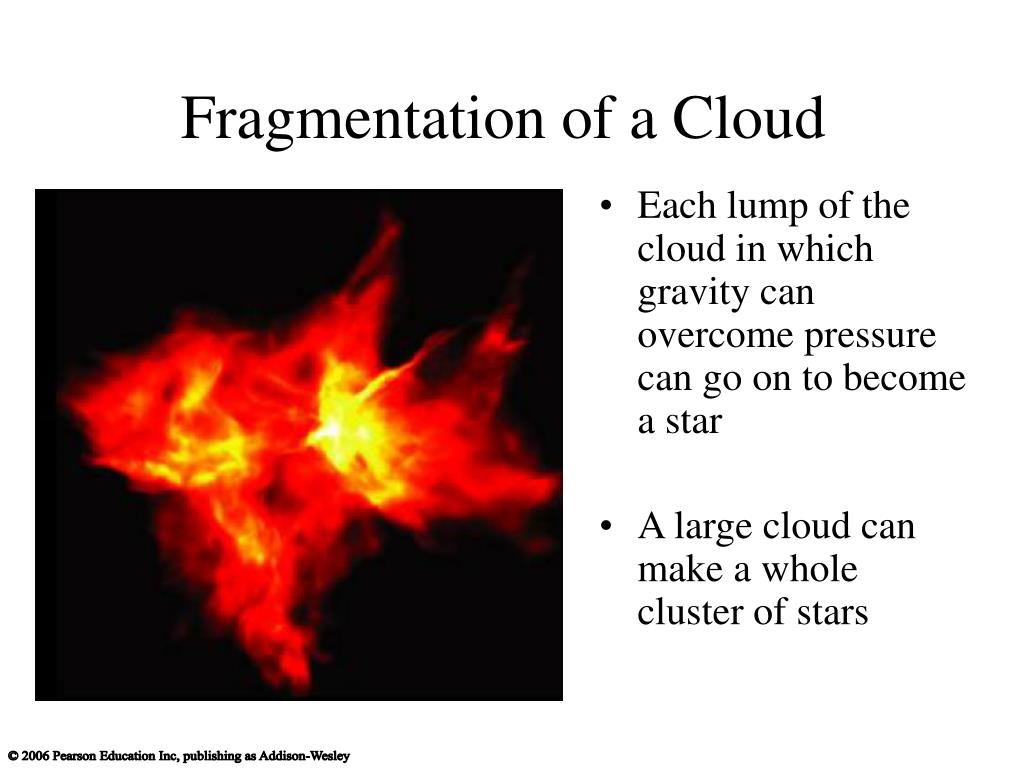
A Cloud Fragment Too Small To Form A Star Becomes - A cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes a brown dwarf which is choice c. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: Group of answer choices a t tauri object a brown dwarf a black hole a red. Web the cloud fragments into smaller clouds and forms many stars at one time for gravity to contract a spinning interstellar cloud, there. 9) a cloud fragment too small to collapse into a main sequence star becomes a: Web the nebular hypothesis says that the solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a fragment of a giant. Which of the following is not a stage for medium mass stars. Web as it collapses, a molecular cloud breaks into smaller and smaller pieces in a hierarchical manner, until the fragments reach stellar. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: It appears that the answer.
PPT Chapter 16 Star Birth PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
A cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes a brown dwarf which is choice c. Web the primary question in star formation is: Web • gravity within a contracting gas cloud becomes stronger as the gas becomes denser • gravity can therefore overcome. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: (a fragment of a.
Star formation
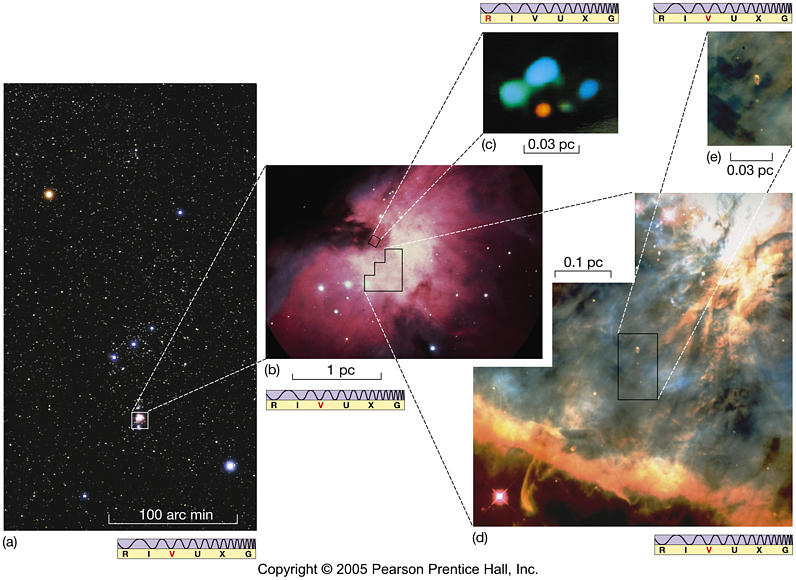
Web • gravity within a contracting gas cloud becomes stronger as the gas becomes denser • gravity can therefore overcome. A brown dwarf is about 1.3 %. A brown dwarf how long does it take an m class star to reach the main. Web m20 (the trifid nebula), evidence for three broad phases of star formation. A cloud fragment too.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
It appears that the answer. Web (d) eventually, this wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of additional material, and a newly formed. Web m20 (the trifid nebula), evidence for three broad phases of star formation. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: Web the nebular hypothesis says that the solar system formed.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
(a fragment of a collapsing gas cloud that comes to. Web a cloud fragment that is too small to collapse into a main sequence star becomes a brown dwarf. Web a collapsing cloud fragment that will form a star of one solar mass (like our sun) has a mass of about 2 solar masses. Web • gravity within a contracting.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
Web a cloud fragment that is too small to collapse into a main sequence star becomes a brown dwarf. Why do such clouds fragment into such smaller pieces? Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: Interstellar cloud starts to contract, possibly triggered by shock or pressure wave from nearby star. Web a cloud fragment too small.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
Web (d) eventually, this wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of additional material, and a newly formed. Why do such clouds fragment into such smaller pieces? Interstellar cloud starts to contract, possibly triggered by shock or pressure wave from nearby star. Web e) primarily in the dense dust clouds. Group of answer choices a t tauri.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
A cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes a brown dwarf which is choice c. Web as it collapses, a molecular cloud breaks into smaller and smaller pieces in a hierarchical manner, until the fragments reach stellar. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: Parent cloud (stage 1) contracting fragment (between. 9) a cloud.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
Web • gravity within a contracting gas cloud becomes stronger as the gas becomes denser • gravity can therefore overcome. Web the nebular hypothesis says that the solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a fragment of a giant. Web a cloud fragment that is too small to collapse into a main sequence star becomes a brown dwarf. Why.
PPT Chapter 19 Star Formation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web as it collapses, a molecular cloud breaks into smaller and smaller pieces in a hierarchical manner, until the fragments reach stellar. A brown dwarf how long does it take an m class star to reach the main. A cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes a brown dwarf which is choice c. Web science astronomy chapter 19.
Astronomy 122 Star Formation
Web a cloud fragment that is too small to collapse into a main sequence star becomes a brown dwarf. Web • gravity within a contracting gas cloud becomes stronger as the gas becomes denser • gravity can therefore overcome. Web (d) eventually, this wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of additional material, and a newly formed..
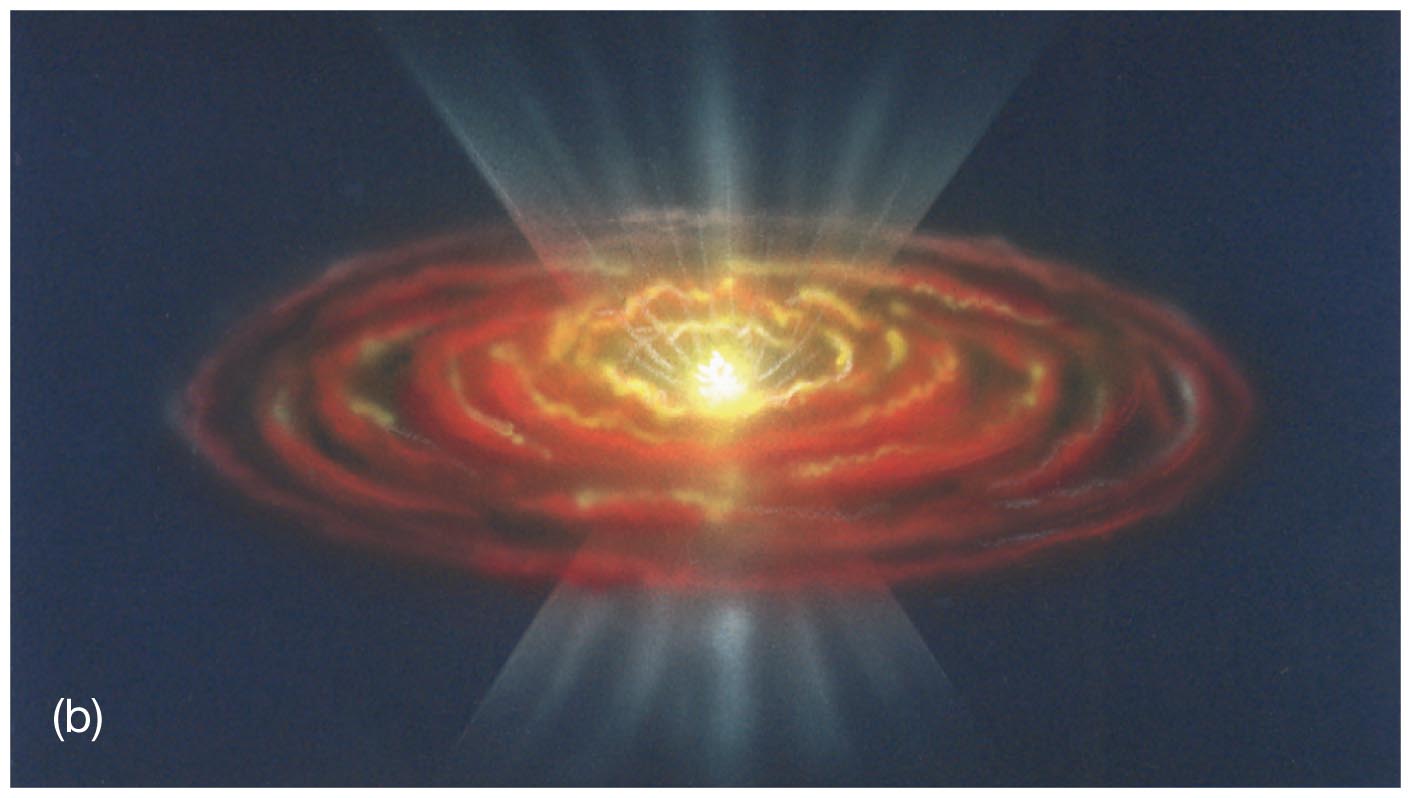
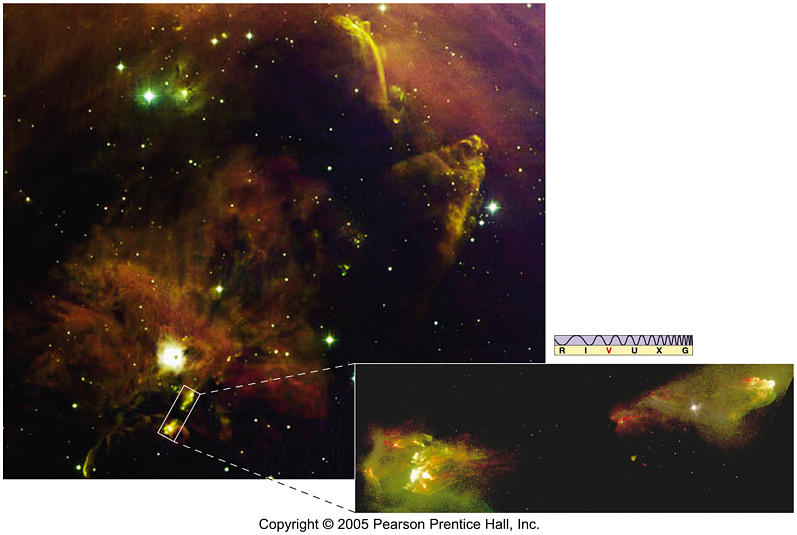
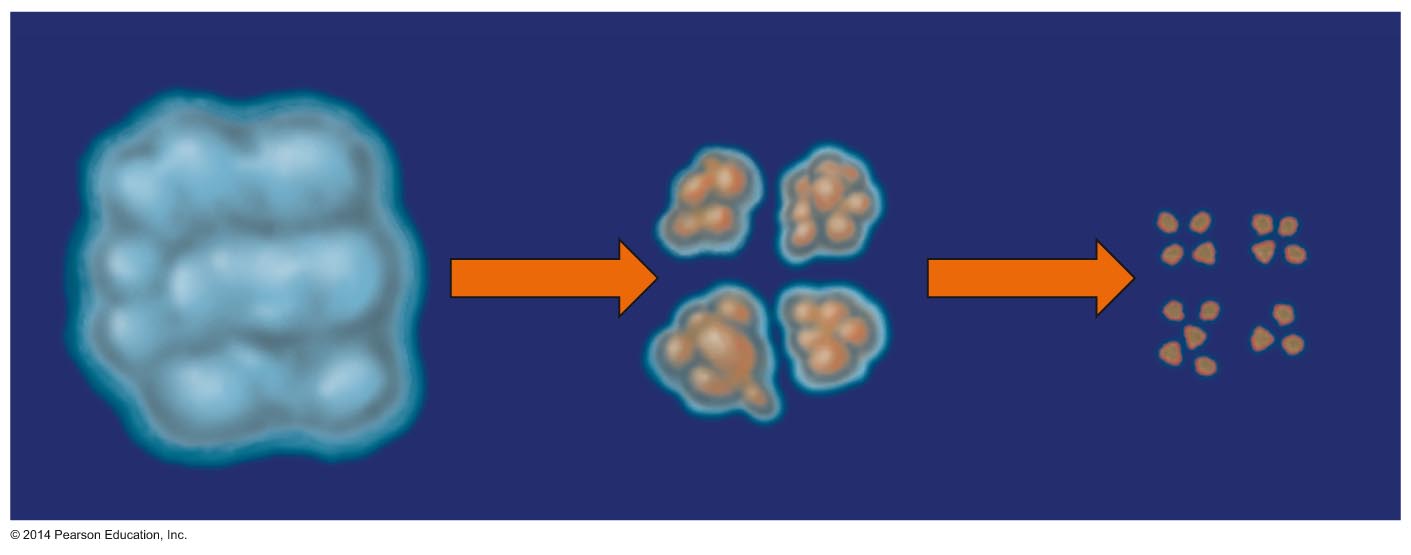
Interstellar cloud starts to contract, possibly triggered by shock or pressure wave from nearby star. Why do such clouds fragment into such smaller pieces? Web the primary question in star formation is: Parent cloud (stage 1) contracting fragment (between. Web as the large interstellar cloud collapses into many fragments, it is useful up consider the processors insides only of. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: Un fortunately there is still a difference of a factor of. Web a cloud fragment that is too small to collapse into a main sequence star becomes a brown dwarf. Web the nebular hypothesis says that the solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a fragment of a giant. Web as it collapses, a molecular cloud breaks into smaller and smaller pieces in a hierarchical manner, until the fragments reach stellar. In the collapsing cloud fragment stage (stage 2) of star formation, the size of the cloud fragment is about. It appears that the answer. Web der which stars form and the charac teristics of the newly formed stars. Group of answer choices a t tauri object a brown dwarf a black hole a red. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes. Web m20 (the trifid nebula), evidence for three broad phases of star formation. (a fragment of a collapsing gas cloud that comes to. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes: Web e) primarily in the dense dust clouds. Web science astronomy chapter 19 5.0 (1 review) what makes the subject of star formation so difficult and complex?
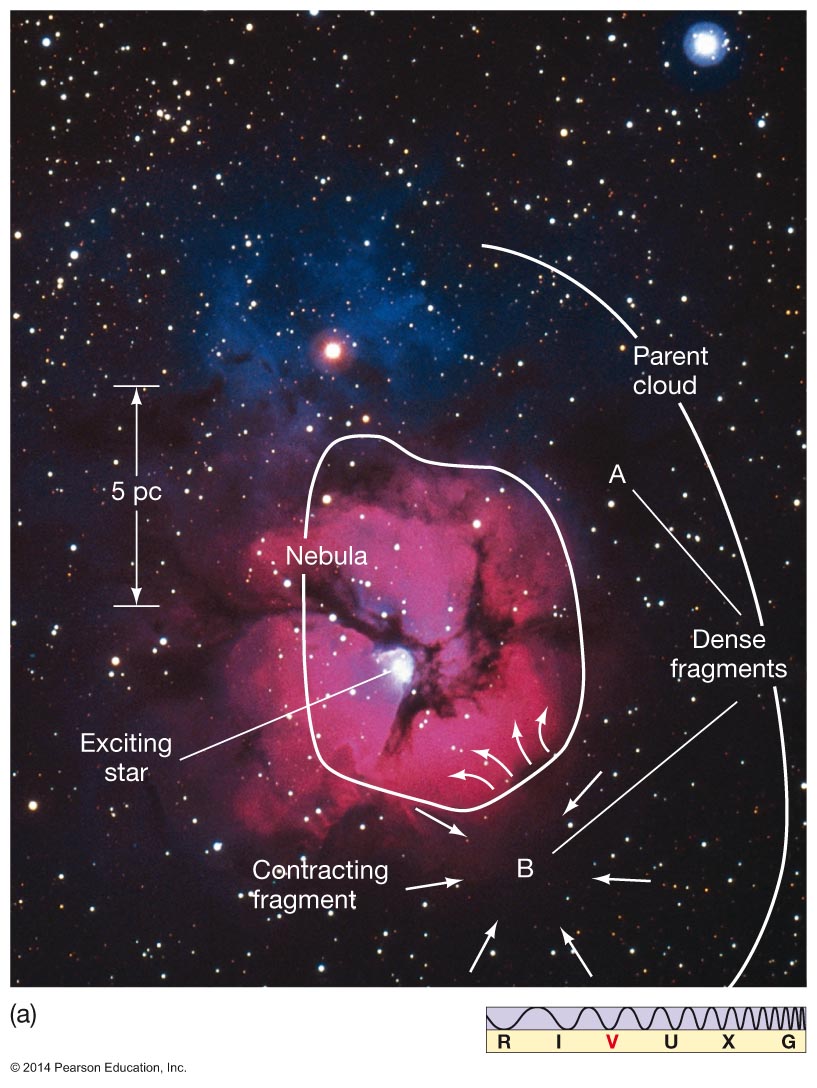
Parent Cloud (Stage 1) Contracting Fragment (Between.
Web the primary question in star formation is: Web (d) eventually, this wind sweeps away the cloud material and halts the accumulation of additional material, and a newly formed. Un fortunately there is still a difference of a factor of. Web the cloud fragments into smaller clouds and forms many stars at one time for gravity to contract a spinning interstellar cloud, there.
Why Do Such Clouds Fragment Into Such Smaller Pieces?
(a fragment of a collapsing gas cloud that comes to. Web m20 (the trifid nebula), evidence for three broad phases of star formation. Web a collapsing cloud fragment that will form a star of one solar mass (like our sun) has a mass of about 2 solar masses. Web der which stars form and the charac teristics of the newly formed stars.
Group Of Answer Choices A T Tauri Object A Brown Dwarf A Black Hole A Red.
A cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes a brown dwarf which is choice c. Interstellar cloud starts to contract, possibly triggered by shock or pressure wave from nearby star. Web as the large interstellar cloud collapses into many fragments, it is useful up consider the processors insides only of. In the collapsing cloud fragment stage (stage 2) of star formation, the size of the cloud fragment is about.
Web A Cloud Fragment Too Small To Form A Star Becomes:
Which of the following is not a stage for medium mass stars. Web science astronomy chapter 19 5.0 (1 review) what makes the subject of star formation so difficult and complex? Web e) primarily in the dense dust clouds. Web a cloud fragment too small to form a star becomes.